Page 441 - IJB-9-2
P. 441
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinting of DNA hydrogels for bone organoids
accuracy (reach to 1 µm) or fast printing speed (ranging
from 25 to 1000 mm/min) of this technology. Higher speed
can be obtained at the expense of accuracy. The process
chiefly relies on the light power intensity and the inherent
properties of printing material . Due to their satisfying
[4]
biocompatibility, good adaptability, and controllable
biodegradability, soft biomaterials such as hydrogels have
opened up a broad insight into tissue regeneration, drug
delivery, and bio-actuators . With the rapid development
[5]
of DLP-based 3D printing technology, hydrogels have been
fabricated into sophisticated architectures (e.g., biomimetic
scaffolds) for bone regeneration. However, traditional
hydrogels generally undergo rapid biodegradation and have
weak mechanical properties. Thus, the design principles
of traditional hydrogels based on DLP technology do
not take into consideration the biomimetic regulation
of multiple stages throughout the bone healing, and the
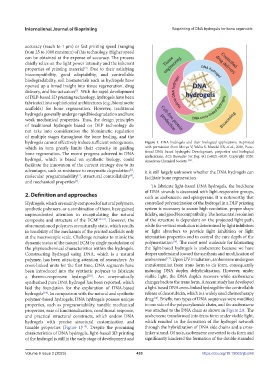
hydrogels cannot effectively induce sufficient osteogenesis, Figure 1. DNA hydrogels and their biological applications. Reprinted
which in turn greatly limits their capacity in guiding with permission from Morya V, Walia S, Mandal BB, et al., 2020, Func-
bone regeneration. The recent progress achieved in DNA tional DNA based hydrogels: Development, properties and biological
applications. ACS Biomater Sci Eng, 6(11):6021–6035. Copyright 2020.
hydrogel, which is based on synthetic biology, could American Chemical Society. .
[15]
facilitate the innovation of the current strategy due to its
advantages, such as resistance to enzymatic degradation , it is still largely unknown whether the DNA hydrogels can
[6]
molecular programmability , structural controllability , facilitate bone regeneration.
[8]
[7]
and mechanical properties .
[9]
To fabricate light-based DNA hydrogels, the backbone
of DNA strands is decorated with light-responsive groups,
2. Definition and approaches such as azobenzene and spiropyrans. It is noteworthy that
Hydrogels, which are mainly composed of natural polymers, controlled polymerization of the hydrogel in a DLP printing
synthetic polymers, or a combination of them, have gained system is necessary to secure high resolution, proper shape
unprecedented attention in recapitulating the natural fidelity, and good biocompatibility. The horizontal resolution
composite and structure of the ECM [10-12] . However, the of the structure is dependent on the projected light path,
aforementioned polymers are naturally static, which results while the vertical resolution is determined by light inhibitors
in tunability of the mechanics of the printed scaffolds only or light absorbers to provide light inhibition or light
at the macroscopic scale. Challenge remains to mimic the attenuation properties and to control the cure depth of the
[16]
dynamic status of the natural ECM by single modulation of polymerization . The most used molecule for fabricating
the physicochemical characteristics within the hydrogels. the light-based hydrogels is azobenzene because we have
Constructing hydrogel using DNA, which is a natural deeper understand toward the synthesis and modification of
polymer, has been attracting attention of researchers. As azobenzene . Upon UV irradiation, azobenzene undergoes
[17]
cross-linked units for the first time, DNA segments have transformation from trans form to cis form, consequently
been introduced into the synthetic polymer to fabricate inducing DNA duplex dehybridization. However, under
a thermo-responsive hydrogel . An enzymatically visible light, the DNA duplex recovers while azobenzene
[13]
synthesized pure DNA hydrogel has been reported, which changes back to the trans form. A recent study has developed
laid the foundation for the exploration of DNA-based a light-based DNA cross-linked hydrogel for the controllable
hydrogels . In comparison with the natural and synthetic release of doxorubicin, which is a widely used chemotherapy
[14]
polymer-based hydrogels, DNA hydrogels possess unique drug . Briefly, two types of DNA sequences were modified
[18]
properties, such as programmability, tunable mechanical to one side of the polyacrylamide chain, and the azobenzene
properties, ease of functionalization, conditional response, was attached to the DNA chain as shown in Figure 2A. The
and practical structural constructs, which endow DNA azobenzene transformed into trans form under visible light,
hydrogels with precise structural customization and which resulted in the formation of the hydrogel network
tunable properties (Figure 1) . Despite the promising through the hybridization of DNA side chains and a cross-
[15]
characteristics of DNA hydrogels, light-based 3D printing linker strand. Of note, azobenzene converted to cis form and
of the hydrogel is still in the early stage of development and significantly hindered the formation of the double-stranded
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 433 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.688