Page 398 - IJB-9-3
P. 398
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinting of a multicellular model
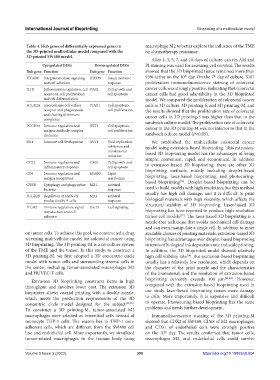
Table 4. Hub genes of differentially expressed genes in macrophage M2 to better explore the influence of the TME
the 3D-printed multicellular model compared with the on chemotherapy resistance.
3D-printed SW480 model.
After 1, 3, 5, 7, and 10 days of culture, calcein AM and
Upregulated DEGs Downregulated DEGs PI staining was used for assessing cell survival. The results
Hub gene Function Hub gene Function showed that the 3D bioprinted tissue remained more than
th
th
ITGAM Integrins mediate signaling DDX58 Innate immune 95% active on the 10 day. On the 7 day of culture, Ki67
and cell adhesion response proliferation immunofluorescence staining of colorectal
IL1B Inflammation regulation, cell OASL Cell growth and cancer cells was strongly positive, indicating that colorectal
apoptosis, cell proliferation cell apoptosis cancer cells had good adaptability in the 3D bioprinted
and cell differentiation model. We compared the proliferation of colorectal cancer
FCGR2A macrophages cell surface STAT1 Cell apoptosis, cells in 3D culture, 3D printing-S, and 3D printing-M, and
receptor and phagocytosis cell proliferation the results showed that the proliferation rate of colorectal
and clearing of immune cancer cells in 3D printing-S was higher than that in the
complexes
FCGR3A Immune regulation and IFIT3 Cell apoptosis, sandwich culture model. The proliferation rate of colorectal
cancer in the 3D printing-M was not inferior to that in the
antigen-antibody complex cell proliferation
clearance sandwich culture model (P<0.05).
SPI1 Immune cell development IFIT1 Viral replication We established the multicellular colorectal cancer
inhibition and model using extrusion-based bioprinting. This extrusion-
translational based 3D bioprinting model has the advantages of being
initiation
simple, convenient, rapid, and economical. In addition
CCL2 Immune regulation and OAS1 Cell growth and to extrusion-based 3D bioprinting, there are other 3D
inflammatory response cell apoptosis
CD4 Immune regulation and RSAD2 Lipid bioprinting methods, mainly including droplet-based
bioprinting, laser-based bioprinting, and photocuring-
antigen recognition metabolism [36]
CYBB Cytophagy and phagocytize MX1 antiviral based bioprinting . Droplet-based bioprinting can be
bacteria response used to build models with high resolution, but this method
FCGR2B Regulation of antibody MX2 antiviral usually has high cell damage, and it is difficult to print
production by B-cells response biological materials with high viscosity, which affects the
ITGB2 Immune regulation, signal ISG15 Cell signaling structural stability of 3D bioprinting. Laser-based 3D
transduction and cell bioprinting has been reported to produce high-resolution
[37]
adhesion tumor cell models . The laser-based 3D bioprinting is a
nozzle-free technique that avoids mechanical cell damage
and can even manipulate a single cell. In addition to more
on tumor cells. To achieve this goal, we constructed a drug available choices of printing materials, extrusion-based 3D
screening multicellular model for colorectal cancer using bioprinting has advantages over droplet-based bioprinting
3D bioprinting. The 3D printing-M is a co-culture system in terms of biological ink deposition rate and scale printing.
of the TME and the tumor. In this study, to construct a In addition, the 3D bioprinted model showed relatively
3D printing-M, we first adopted a 3D concentric circle high cell viability rate . But extrusion-based bioprinting
[18]
model with tumor cells and surrounding stromal cells in usually has a relatively low resolution, which depends on
the center, including tumor-associated macrophages M2 the diameter of the print nozzle and the characteristics
and HUVEC-T cells. of the biomaterial, and the resolution of extrusion-based
Extrusion 3D bioprinting constructs items in high bioprinting currently exceeds 100 µm [32,38] . However,
throughput and involves lower cost. The extrusion 3D compared with the extrusion-based bioprinting used in
bioprinter allows coaxial printing with a double nozzle, our study, laser-based bioprinting causes more damage
which meets the production requirements of the 3D to cells. More importantly, it is expensive and difficult
concentric circle model designed for the subject [34,35] . to operate. Photocuring-based bioprinting has the same
To construct a 3D printing-M, tumor-associated M2 problems and needs further development.
macrophages were selected as interstitial cells instead of Immunofluorescence staining of the 3D printing-M
monocyte THP-1 cells. The reason lies in THP-1 non- showed that CDX2 of SW480, CD68 of M2 macrophages,
adherent cells, which are different from the SW480 cell and CD31 of endothelial cells were strongly positive
line and endothelial cell. More importantly, we simulated on the 10 day. The results confirmed that tumor cells,
th
tumor-related macrophages in the human body using macrophages M2, and endothelial cells could survive
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 390 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.694