Page 147 - IJB-9-5
P. 147
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printed PEEK scaffold mediates macrophages to affect osseointegration
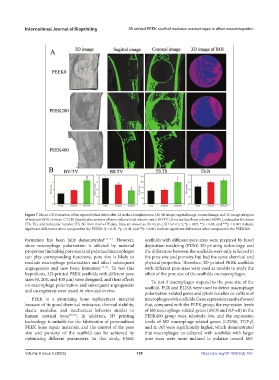
Figure 7. Micro-CT evaluation of the repaired tibial defect after 12 weeks of implantation. (A) 3D image, sagittal image, coronal image, and 3D image of region
of interest (ROI) of micro-CT. (B) Quantitative analysis of bone volume/total volume ratio (BV/TV), bone surface/bone volume (BS/BV), trabecular thickness
(Tb. Th), and trabecular number (Tb. N) from micro-CT data. Data are shown as the mean ± SD for n ≥ 3; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 indicate
significant differences when compared to the PEEK0; p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001 indicate significant differences when compared to the PEEK200.
##
###
#
formation has been fully demonstrated [35-37] . However, scaffolds with different pore sizes were prepared by fused
since macrophage polarization is affected by material deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing technology, and
properties (including pore size) and polarized macrophages the differences between the scaffolds were only reflected in
can play corresponding functions, pore size is likely to the pore size and porosity, but had the same chemical and
mediate macrophage polarization and affect subsequent physical properties. Therefore, 3D-printed PEEK scaffolds
angiogenesis and new bone formation [17,19] . To test this with different pore sizes were used as models to study the
hypothesis, 3D-printed PEEK scaffolds with different pore effect of the pore size of the scaffolds on macrophages.
sizes (0, 200, and 400 μm) were designed, and their effects To test if macrophages respond to the pore size of the
on macrophage polarization and subsequent angiogenesis scaffold, PCR and ELISA were used to detect macrophage
and osteogenesis were tested in vitro and in vivo.
polarization-related genes and cytokines after co-culture of
PEEK is a promising bone replacement material macrophages with scaffolds. Gene expression results showed
because of its good chemical resistance, thermal stability, that, compared with the PEEK group, the expression levels
elastic modulus, and mechanical behavior similar to of M1 macrophage-related genes (iNOS and NF-κB) in the
human cortical bone [38,39] . In addition, 3D printing PEEK400 group were relatively low, and the expression
technology is suitable for the fabrication of personalized levels of M2 macrophage-related genes (CD206, TGF-β,
PEEK bone repair materials, and the control of the pore and IL-10) were significantly higher, which demonstrated
size and porosity of the scaffold can be achieved by that macrophages co-cultured with scaffolds with larger
optimizing different parameters. In this study, PEEK pore sizes were more inclined to polarize toward M2-
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 139 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.755