Page 204 - IJB-9-5
P. 204
International Journal of Bioprinting Using droplet jetting for bioprinting
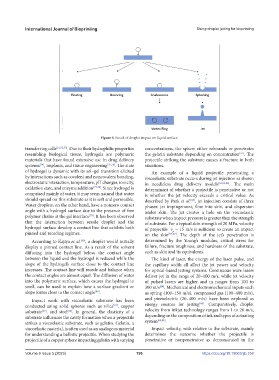
Figure 4. Result of droplet impact on liquid surface.
transferring cells [21,72,73] . Due to their hydrophilic properties concentrations, the sphere either rebounds or penetrates
resembling biological tissue, hydrogels are polymeric the gelatin substrate depending on concentration . The
[57]
materials that have found extensive use in drug delivery projectile striking the substrate causes a fracture in both
systems , implants, and tissue engineering [75,76] . The state situations.
[74]
of hydrogel is dynamic with its sol–gel transition elicited An example of a liquid projectile penetrating a
by interactions such as covalent and noncovalent bonding, viscoelastic substrate occurs during jet injection as shown
electrostatic interaction, temperature, pH changes, ionicity, in needleless drug delivery models [56,83,84] . The main
oxidation state, and enzyme addition [77,78] . Since hydrogel is determinant of whether a projectile is penetrative or not
comprised mainly of water, it may seem natural that water is whether the jet velocity exceeds a critical value. As
should spread on this substrate as it is soft and permeable. described by Park et al. , jet injection consists of three
[85]
Water droplets, on the other hand, have a nonzero contact phases: jet impingement, flow into skin, and dispersion
angle with a hydrogel surface due to the presence of free under skin. The jet creates a hole on the viscoelastic
polymer chains at the gel interface . It has been observed substrate when impact pressure is greater than the strength
[79]
that the interaction between sessile droplet and the of substrate. For a typical skin strength of 20 MPa, velocity
hydrogel surface develop a contact line that exhibits both of projectile v ~ 15 m/s is sufficient to create an impact
p
pinned and receding regimes. on the skin [85-87] . The depth of the jet’s penetration is
According to Kajiya et al. , a droplet would initially determined by the Young’s modulus, critical stress for
[80]
display a pinned contact line. As a result of the solvent failure, fracture toughness, and hardness of the substrate,
diffusing into the hydrogel below, the contact angle such as skin and its equivalents.
between the liquid and the hydrogel is reduced while the The kind of laser, the energy of the laser pulse, and
slope of the hydrogel’s surface close to the contact line the capillary width all affect the jet power and velocity
increases. The contact line will recede and balance when for optical-based jetting systems. Continuous wave lasers
the contact angles are almost equal. The diffusion of water deliver jet in the range of 20–100 m/s, while jet velocity
into the polymeric surface, which causes the hydrogel to of pulsed lasers are higher and in ranges from 100 to
swell, can be used to explain how a surface gradient or 300 m/s . Mechanical and electromechanical inputs such
[84]
slope forms close to the contact angle . as spring (100–150 m/s), compressed gas (100–400 m/s),
[80]
Impact work with viscoelastic substrate has been and piezoelectric (20–400 m/s) have been explored as
[84]
conducted using solid spheres such as silica , copper energy sources for jetting . Comparatively, droplet
[81]
substrate , and steel . In general, the elasticity of a velocity from inkjet technology ranges from 1 to 20 m/s,
[57]
[82]
substrate influences the cavity formation when a projectile depending on the composition of ink and types of actuating
strikes a viscoelastic substrate, such as gelatin. Gelatin, a system [60,88] .
viscoelastic material, is often used as an analogous material Impact velocity, with relative to the substrate, mainly
for understanding a ballistic projectile. When studying the determines the outcome whether the projectile is
projectile of a copper sphere impacting gelatin with varying penetrative or nonpenetrative as demonstrated in the
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 196 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.758