Page 208 - IJB-9-5
P. 208
International Journal of Bioprinting Using droplet jetting for bioprinting
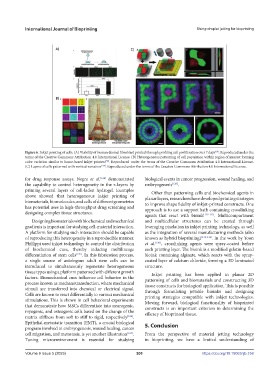
Figure 6. Inkjet printing of cells. (A) Viability of human dermal fibroblast printed through profiling cell proliferation over 7 days . Reproduced under the
[60]
terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. (B) Heterogeneous patterning of cell population within region of interest forming
color variation similar to home-based inkjet printers . Reproduced under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
[58]
(C) Layers of cells patterned with vertical variation [124] . Reproduced under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
for drug response assays. Negro et al. [124] demonstrated biological events in cancer progression, wound healing, and
the capability to control heterogeneity in the z-layers by embryogenesis [128] .
printing several layers of cell-laden hydrogel. Examples Other than patterning cells and biochemical agents in
above showed that heterogeneous inkjet printing of planar layers, researchers have developed printing strategies
biomaterials, biomolecules, and cells of different geometries to improve shape fidelity of inkjet-printed constructs. One
has potential uses in high-throughput drug screening and approach is to use a support bath containing crosslinking
designing complex tissue structures. agents that react with bioink [129-131] . Multicompartment
Designing biomaterials with biochemical and mechanical and multicellular structures can be created through
gradients is important for studying cell-material interaction. leveraging pixelation in inkjet printing technology, as well
A platform for studying such interaction should be capable as the integration of several manufacturing methods (also
of reproducing this heterogeneity in a reproducible manner. known as hybrid bioprinting) [132-134] . In the work by Yoon
Phillippi used inkjet technology to control the distribution et al. [130] , crosslinking agents were spray-coated before
of biochemical cues, thereby inducing multilineage each printing layer. The bioink is a modified gelatin-based
differentiation of stem cells [125] . In this fabrication process, bioink containing alginate, which reacts with the spray-
a single source of autologous adult stem cells can be coated layer of calcium chloride, forming a 3D laminated
introduced to simultaneously regenerate heterogeneous structure.
tissue types using a platform patterned with different growth Inkjet printing has been applied in planar 2D
factors. Biomechanical cues influence cell behavior in the patterning of cells and biomaterials and constructing 3D
process known as mechanotransduction, where mechanical tissue constructs for biological application. This is possible
stimuli are transferred into chemical or electrical signal. through formulating jettable bioinks and designing
Cells are known to react differentially to various mechanical printing strategies compatible with inkjet technologies.
stimulations. This is shown in cell behavioral experiments Moving forward, biological functionality of bioprinted
that demonstrate how MSCs differentiate into neurogenic, constructs is an important criterion in determining the
myogenic, and osteogenic cells based on the change of the efficacy of bioprinted tissue.
matrix stiffness from soft to stiff to rigid, respectively [126] .
Epithelial-metastatic transition (EMT), a crucial biological 5. Conclusion
program involved in embryogenesis, wound healing, cancer
cell migration, and metastasis, is yet another illustration [127] . From the perspective of material jetting technology
Tuning microenvironment is essential for studying in bioprinting, we have a limited understanding of
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 200 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.758