Page 371 - IJB-9-5
P. 371
International Journal of Bioprinting Multifunctional hydrogel surgical training model
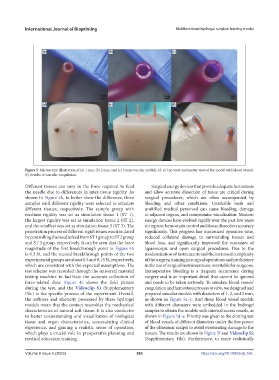
Figure 5. Microscopic illustration of (a) 1 mm, (b) 2 mm, and (c) 3 mm vascular models. (d, e) Top view and master view of the model with blood vessels.
(f) Results of vascular coagulation.
Different tissues can vary in the force required to feed Surgical energy devices that provide adequate hemostasis
the needle due to differences in inter-tissue rigidity. As and allow accurate dissection of tissue are critical during
shown in Figure 4b, to better show the difference, three surgical procedures, which are often accompanied by
samples with different rigidity were selected to simulate bleeding and other conditions. Unreliable tools and
different tissues, respectively. The sample group with unskilled medical personnel can cause bleeding, damage
medium rigidity was set as simulation tissue 1 (ST 1), to adjacent organs, and compromise visualization. Modern
the largest rigidity was set as simulation tissue 2 (ST 2), energy devices have evolved rapidly over the past few years
and the smallest was set as simulation tissue 3 (ST 3). The to improve hemostasis control and tissue dissection accuracy
penetration process of different rigid tissues was simulated significantly. This progress has minimized operative time,
by controlling the needle feed from ST 1 group to ST 2 group reduced collateral damage to surrounding tissues and
and ST 3 group, respectively. It can be seen that the force blood loss, and significantly improved the outcomes of
magnitude of the first breakthrough point in Figure 4b laparoscopic and open surgical procedures. Due to the
is 0.3 N, and the second breakthrough points of the two modernization of instruments and the increased complexity
experimental groups are about 0.5 and 0.15 N, respectively, of the surgery, training in surgical operations and proficiency
which are consistent with the expected assumptions. The in the use of surgical instruments are inevitable for surgeons.
test scheme was recorded through the universal material Intraoperative bleeding is a frequent occurrence during
testing machine to facilitate the accurate collection of surgery and is an important detail that cannot be ignored
force-related data. Figure 4c shows the field picture and needs to be taken seriously. To simulate blood vessels’
during the test, and the Videoclip S1 (Supplementary coagulation and hemostasis process in vitro, we designed and
File) is the specific process of the experiment. Overall, prepared vascular models with diameters of 1, 2, and 3 mm,
the softness and elasticity possessed by these hydrogel as shown in Figure 5a–c. And these blood vessel models
models mean that the contact resembles the mechanical with different diameters were embedded in the hydrogel
characteristics of natural soft tissue. It is also conducive samples to obtain the models with internal access vessels, as
to better understanding and visualization of biological shown in Figure 5d–e. Priority was given to the clotting test
tissue and organ characteristics, accumulating clinical of blood vessels of different diameters under the low power
experience, and gaining a realistic sense of operation, of the ultrasonic scalpel to avoid overheating damage to the
which plays a crucial role in preoperative planning and tissues. The results are shown in Figure 5f and Videoclip S2
medical education training. (Supplementary File). Furthermore, to more realistically
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 363 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.766