Page 149 - IJB-9-6
P. 149
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printed bioactive dressings for burn wound treatment
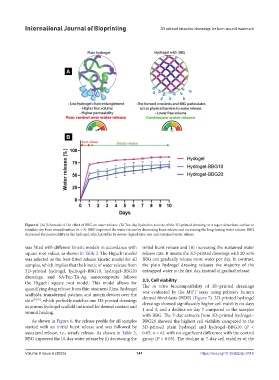
Figure 6. (A) Schematic of the effect of BBG on water release. (B) Ten-day hydration activity of the 3D-printed dressing on a super-absorbent surface to
simulate dry burn wound surface (n = 5). BBG improved the water release by decreasing burst release and increasing the long-lasting water release. BBG
decreased the permeability in the hydrogel, which justifies its slower degradation rate and sustained water release.
was fitted with different kinetic models in accordance with initial burst release and (ii) increasing the sustained water
square root values, as shown in Table 2. The Higuchi model release rate. It means the 3D-printed dressings with 20 wt%
was selected as the best-fitted release kinetic model for all BBG can gradually release more water per day. In contrast,
samples, which implies that the kinetic of water release from the plain hydrogel dressing releases the majority of the
3D-printed hydrogel, hydrogel–BBG10, hydrogel–BBG20 entrapped water at the first day, instead of gradual release.
dressings, and SA/Pec/TA-Ag nanocomposite follows
the Higuchi square root model. This model allows for 3.5. Cell viability
quantifying drug release from thin ointment films, hydrogel The in vitro biocompatibility of 3D-printed dressings
scaffolds, transdermal patches, and matrix devices over the was evaluated by the MTT assay using primary human
dermal fibroblasts (HDF) (Figure 7). 3D-printed hydrogel
skin [78,79] , which perfectly matches our 3D-printed dressings
as porous hydrogel scaffold indicated for dermal contact and dressings showed significantly higher cell viability on days
1 and 3, and a decline on day 7 compared to the samples
wound healing.
with BBG. The 7-day extracts from 3D-printed hydrogel–
As shown in Figure 6, the release profile for all samples BBG20 showed the highest cell viability compared to the
started with an initial burst release and was followed by 3D-printed plain hydrogel and hydrogel–BBG10 (P <
sustained release, i.e., steady release. As shown in Table 2, 0.05, n = 6), with no significant difference with the control
BBG improved the 10-day water release by (i) decreasing the group (P > 0.05). The decline in 7-day cell viability of the
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 141 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0118