Page 449 - IJB-9-6
P. 449
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting for lung tissue
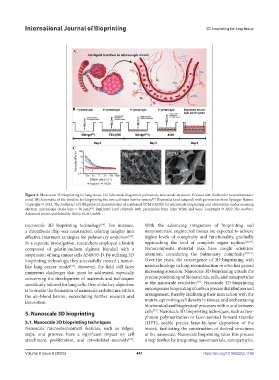
Figure 3. Microscale 3D bioprinting for lung tissue. (A) Schematic diagram of pulmonary microscale structure. Created with BioRender (www.biorender.
[60]
com). (B) Schematic of the timeline for bioprinting the two cell-layer barrier system . Reprinted (and adapted) with permission from Springer Nature.
Copyright © 2015, The Author(s). (C) Biophysical characteristics of reinforced ECM (rECM) for microscale bioprinting and observation under scanning
[62]
electron microscope (scale bars = 50 µm) . Reprinted (and adapted) with permission from John Wiley and Sons. Copyright © 2022 The Authors.
Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
microscale 3D bioprinting technology . For instance, With the advancing integration of bioprinting and
[64]
a thrombosis chip was constructed, offering insights into nanomaterials, engineered tissues are expected to achieve
effective treatment strategies for pulmonary embolism . higher levels of complexity and functionality, gradually
[65]
In a separate investigation, researchers employed a bioink approaching the level of complete organ replicas [68,69] .
composed of gelatin-sodium alginate blended with a Nanocomposite material inks have caught scientists’
suspension of lung cancer cells A549/95-D. By utilizing 3D attention, considering the pulmonary complexity [70,71] .
bioprinting technology, they successfully created a tumor- Over the years, the convergence of 3D bioprinting with
like lung cancer model . However, the field still faces nanotechnology in lung reconstruction in vitro has gained
[66]
numerous challenges that must be addressed, especially increasing attention. Nanoscale 3D bioprinting entails the
concerning the development of materials and techniques precise positioning of biomaterials, cells, and nanoparticles
[72]
specifically tailored for lung cells. One of the key objectives at the nanoscale resolution . Nanoscale 3D bioprinting
is to enable the formation of nanoscale architecture within encompasses bioprinting of cells in precise distribution and
the air–blood barrier, necessitating further research and arrangement, thereby facilitating their interaction with the
innovation. matrix, optimizing cell density in tissues, and orchestrating
biochemical and biophysical processes within and between
[73]
5. Nanoscale 3D bioprinting cells . Nanoscale 3D bioprinting techniques, such as two-
photon polymerization or laser-assisted forward transfer
5.1. Nanoscale 3D bioprinting techniques (LIFT), enable precise layer-by-layer deposition of the
Nanoscale microenvironment features, such as ridges, bioink, facilitating the construction of desired structures
steps, and grooves, have a significant impact on cell at the nanoscale. Nanoscale bioprinting takes this process
attachment, proliferation, and cytoskeletal assembly . a step further by integrating nanomaterials, nanoparticles,
[67]
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 441 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1166