Page 451 - IJB-9-6
P. 451
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting for lung tissue
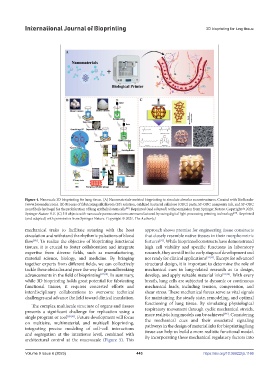
Figure 4. Nanoscale 3D bioprinting for lung tissue. (A) Nanomaterials-assisted bioprinting to simulate alveolar nanostructures. Created with BioRender
(www.biorender.com). (B) Process of fabricating silk fibroin (SF) solution, oxidized bacterial cellulose (OBC) paste, SF-OBC composite ink, and SF-OBC
[80]
nanofibrils hydrogel for the proliferation of lung epithelial stem cells . Reprinted (and adapted) with permission from Springer Nature. Copyright © 2020,
[83]
Springer Nature B.V. (C) 3D objects with nanoscale porous structures are manufactured by using digital light processing printing technology . Reprinted
(and adapted) with permission from Springer Nature. Copyright © 2021, The Author(s).
mechanical traits to facilitate suturing with the host approach shows promise for engineering tissue constructs
circulation and withstand the rhythmic pulsations of blood that closely resemble native tissues in their morphometric
flow . To realize the objective of bioprinting functional features . While bioprinted constructs have demonstrated
[91]
[86]
tissues, it is crucial to foster collaboration and integrate high cell viability and specific functions in laboratory
expertise from diverse fields, such as manufacturing, research, they are still in the early stages of development and
material science, biology, and medicine. By bringing not ready for clinical applications [92,93] . Except for advanced
together experts from different fields, we can collectively structural design, it is important to determine the role of
tackle these obstacles and pave the way for groundbreaking mechanical cues in lung-related research as to design,
advancements in the field of bioprinting [87,88] . In summary, develop, and apply suitable material inks [94,95] . With every
while 3D bioprinting holds great potential for fabricating breath, lung cells are subjected to dynamic or continuous
functional tissues, it requires concerted efforts and mechanical loads, including tension, compression, and
interdisciplinary collaborations to overcome technical shear stress. These mechanical forces serve as vital signals
challenges and advance the field toward clinical translation. for maintaining the steady state, remodeling, and optimal
functioning of lung tissue. By simulating physiological
The complex multiscale structure of organs and tissues
presents a significant challenge for replication using a respiratory movement through cyclic mechanical stretch,
[96]
single program or tool [89,90] . Future development will focus more realistic lung models can be achieved . Considering
on multisize, multimaterial, and multicell bioprinting, the mechanical cues and their associated signaling
integrating precise modeling of cell–cell interactions pathways in the design of material inks for bioprinting lung
and segregation at the intratissue level, combined with tissue can help us build a more realistic functional model.
architectural control at the macroscale (Figure 5). This By incorporating these mechanical regulatory factors into
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 443 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1166