Page 60 - IJB-9-6
P. 60
International Journal of Bioprinting Sub-regional design of the bionic bone scaffolds
Figure 13. Growth rate of S and E for (a) C = 50% and (b) C = 90%.
1
2
As shown in Figure 12c and f, specimens in irregularity
series have an apparent elastic modulus range between
4.67 GPa and 5.83 GPa. E decreases almost linearly as
irregularity increases. Meanwhile, S reaches a value range
of 182.51–216.14 MPa, showing an irregular change trend,
different from E. For instance:
(i) S of the as-built specimen, with ε = 0.12, is equal to
216.14 MPa, which is the maximum value in ε series
whereas the corresponding value of E is 5.62 GPa;
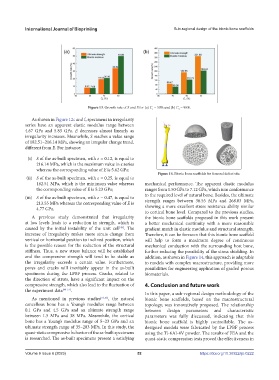
Figure 14. Bionic bone scaffolds for femoral defect site.
(ii) S of the as-built specimen, with ε = 0.25, is equal to
182.51 MPa, which is the minimum value whereas mechanical performance. The apparent elastic modulus
the corresponding value of E is 5.23 GPa; ranges from 1.50 GPa to 7.12 GPa, which is in conformance
(iii) S of the as-built specimen, with ε = 0.47, is equal to to the required level of natural bone. Besides, the ultimate
213.55 MPa whereas the corresponding value of E is strength ranges between 38.55 MPa and 268.03 MPa,
4.77 GPa. showing a more excellent stress resistance ability similar
to cortical bone level. Compared to the previous studies,
A previous study demonstrated that irregularity the bionic bone scaffolds proposed in this work present
at low levels leads to a reduction in strength, which is a better mechanical continuity with a more reasonable
caused by the initial instability of the unit cell . The gradient match in elastic modulus and structural strength.
[48]
increase of irregularity makes more struts change from Therefore, it can be foreseen that this bionic bone scaffold
vertical or horizontal position to inclined position, which will help to form a maximum degree of continuous
is the possible reason for the reduction of the structural mechanical conduction with the surrounding host bone,
stiffness. Thus, a new stress balance will be established further reducing the possibility of the stress shielding. In
and the compressive strength will tend to be stable as addition, as shown in Figure 14, this approach is adaptable
the irregularity exceeds a certain value. Furthermore, to models with complex macrostructure, providing more
pores and cracks will inevitably appear in the as-built possibilities for engineering application of graded porous
specimens during the LPBF process. Cracks, related to biomaterials.
the direction of struts, have a significant impact on the
compressive strength, which also lead to the fluctuation of 4. Conclusion and future work
the experiment data [49-51] .
In this paper, a sub-regional design methodology of the
As mentioned in previous studies [52,53] , the natural bionic bone scaffolds, based on the macrostructural
cancellous bone has a Young’s modulus range between topology, was innovatively proposed. The relationship
0.1 GPa and 4.5 GPa and an ultimate strength range between design parameters and characteristic
between 1.5 MPa and 38 MPa. Meanwhile, the cortical parameters was fully discussed, indicating that this
bone has a Young’s modulus range of 5–23 GPa and an bionic bone scaffold is highly controllable. The as-
ultimate strength range of 35–283 MPa. In this study, the designed models were fabricated by the LPBF process
quasi-static compressive behavior of the as-built specimens using the Ti-6Al-4V powder. The results of FEA and the
is researched. The as-built specimens present a satisfying quasi-static compression tests proved the effectiveness in
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 52 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0222