Page 14 - ITPS-6-1
P. 14
8 INNOSC Theranostics and Pharmacological Sciences, 2023, Vol. 6, No. 1 Vishwakarma, et al.
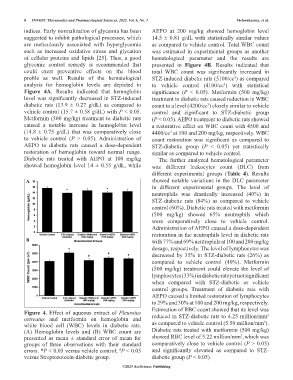
indices. Early normalization of glycemia has been AEPO at 200 mg/kg showed hemoglobin level
suggested to inhibit pathological processes, which 14.5 ± 0.81 g/dL with statistically similar values
are meticulously associated with hyperglycemia as compared to vehicle control. Total WBC count
such as increased oxidative stress and glycation was estimated in experimental groups as another
of cellular proteins and lipids [25]. Thus, a good hematological parameter and the results are
glycemic control remedy is recommended that presented in Figure 4B. Results indicated that
could exert preventive effects on the blood total WBC count was significantly increased in
profile as well. Results of the hematological STZ-induced diabetic rats (5100/cc ) as compared
3
analysis for hemoglobin levels are depicted in to vehicle control (4100/cc ) with statistical
3
Figure 4A. Results indicated that hemoglobin significance (P < 0.05). Metformin (500 mg/kg)
level was significantly decreased in STZ-induced treatment to diabetic rats caused reduction in WBC
diabetic rats (13.9 ± 0.27 g/dL) as compared to count to a level (4200/cc ) closely similar to vehicle
3
vehicle control (15.7 ± 0.58 g/dL) with P < 0.05. control and significant to STZ-diabetic group
Metformin (500 mg/kg) treatment to diabetic rats (P < 0.05). AEPO treatment to diabetic rats showed
caused a notable increase in hemoglobin level a restorative effect on WBC count with 4500 and
(14.8 ± 0.75 g/dL) that was comparatively close 4400/cc at 100 and 200 mg/kg, respectively. WBC
3
to vehicle control (P > 0.05). Administration of count restoration was significant as compared to
AEPO to diabetic rats caused a dose-dependent STZ-diabetic group (P < 0.05) yet statistically
restoration of hemoglobin toward normal range. similar as compared to vehicle control.
Diabetic rats treated with AEPO at 100 mg/kg The further analyzed hematological parameter
showed hemoglobin level 14 ± 0.55 g/dL, while was different leukocytes count (DLC) from
different experimental groups (Table 4). Results
A showed notable variations in the DLC parameter
in different experimental groups. The level of
neutrophils was drastically increased (40%) in
STZ-diabetic rats (84%) as compared to vehicle
control (60%). Diabetic rats treated with metformin
(500 mg/kg) showed 65% neutrophils which
were comparatively close to vehicle control.
Administration of AEPO caused a dose-dependent
restoration in the neutrophils level in diabetic rats
B with 77% and 69% neutrophils at 100 and 200 mg/kg
dosage, respectively. The level of lymphocytes was
decreased by 35% in STZ-diabetic rats (26%) as
compared to vehicle control (40%). Metformin
(500 mg/kg) treatment could elevate the level of
lymphocytes (33%) in diabetic rats yet not significant
when compared with STZ-diabetic or vehicle
control groups. Treatment of diabetic rats with
AEPO caused a limited restoration of lymphocytes
to 29% and 30% at 100 and 200 mg/kg, respectively.
Estimation of RBC count showed that its level was
Figure 4. Effect of aqueous extract of Pleurotus
3
ostreatus and metformin on hemoglobin and reduced in STZ-diabetic rats to 4.25 million/mm
3
white blood cell (WBC) levels in diabetic rats. as compared to vehicle control (5.50 million/mm ).
(A) Hemoglobin levels and (B) WBC count are Diabetic rats treated with metformin (500 mg/kg)
3
presented as mean ± standard error of mean for showed RBC level of 5.22 million/mm ,which was
groups of three observations with their standard comparatively close to vehicle control (P > 0.05)
errors. *P < 0.05 versus vehicle control; P < 0.05 and significantly elevated as compared to STZ-
#
versus Streptozotocin-diabetic group. diabetic group (P < 0.05).
©2023 AccScience Publishing