Page 13 - ITPS-6-1
P. 13
7 INNOSC Theranostics and Pharmacological Sciences, 2023, Vol. 6, No. 1 Vishwakarma, et al.
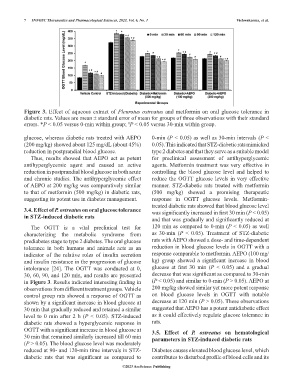
Figure 3. Effect of aqueous extract of Pleurotus ostreatus and metformin on oral glucose tolerance in
diabetic rats. Values are mean ± standard error of mean for groups of three observations with their standard
errors. *P < 0.05 versus 0-min within group; P < 0.05 versus 30-min within group.
#
glucose, whereas diabetic rats treated with AEPO 0-min (P < 0.05) as well as 30-min intervals (P <
(200 mg/kg) showed about 125 mg/dL (about 45%) 0.05). This indicated that STZ-diabetic rats mimicked
reduction in postprandial blood glucose. type 2 diabetes and that they serve as a suitable model
Thus, results showed that AEPO act as potent for preclinical assessment of antihyperglycemic
antihyperglycemic agent and caused an active agents. Metformin treatment was very effective in
reduction in postprandial blood glucose in both acute controlling the blood glucose level and helped to
and chronic studies. The antihyperglycemic effect reduce the OGTT glucose levels in very effective
of AEPO at 200 mg/kg was comparatively similar manner. STZ-diabetic rats treated with metformin
to that of metformin (500 mg/kg) in diabetic rats, (500 mg/kg) showed a promising therapeutic
suggesting its potent use in diabetes management. response in OGTT glucose levels. Metformin-
treated diabetic rats showed that blood glucose level
3.4. Effect of P. ostreatus on oral glucose tolerance was significantly increased in first 30 min (P < 0.05)
in STZ-induced diabetic rats and that was gradually and significantly reduced at
The OGTT is a vital preclinical test for 120 min as compared to 0-min (P < 0.05) as well
characterizing the metabolic syndrome from as 30-min (P < 0.05). Treatment of STZ-diabetic
prediabetes stage to type 2 diabetes. The oral glucose rats with AEPO showed a dose- and time-dependent
tolerance in both humans and animals acts as an reduction in blood glucose levels in OGTT with a
indicator of the relative roles of insulin secretion response comparable to metformin. AEPO (100 mg/
and insulin resistance in the progression of glucose kg) group showed a significant increase in blood
intolerance [24]. The OGTT was conducted at 0, glucose at first 30 min (P < 0.05) and a gradual
30, 60, 90, and 120 min, and results are presented decrease that was significant as compared to 30-min
in Figure 3. Results indicated interesting finding in (P < 0.05) and similar to 0-min (P > 0.05). AEPO at
observations from different treatment groups. Vehicle 200 mg/kg showed similar yet more potent response
control group rats showed a response of OGTT as on blood glucose levels in OGTT with notable
shown by a significant increase in blood glucose at decrease at 120 min (P > 0.05). These observations
30 min that gradually reduced and retained a similar suggested that AEPO has a potent antidiabetic effect
level to 0 min after 2 h (P < 0.05). STZ-induced as it could effectively regulate glucose tolerance in
diabetic rats showed a hyperglycemic response in rats.
OGTT with a significant increase in blood glucose at 3.5. Effect of P. ostreatus on hematological
30 min that remained similarly increased till 60 min parameters in STZ-induced diabetic rats
(P > 0.05). The blood glucose level was moderately
reduced at 90- and 120-min time intervals in STZ- Diabetes causes elevated blood glucose level, which
diabetic rats that was significant as compared to contributes to disturbed profile of blood cells and its
©2023 AccScience Publishing