Page 45 - JCBP-2-3
P. 45
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Emotions in anophthalmic patients
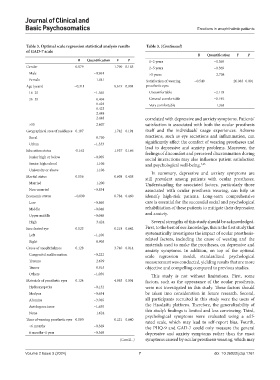
Table 3. Optimal scale regression statistical analysis results Table 3. (Continued)
of GAD‑7 scale
Β Quantification F P
Β Quantification F P 1–2 years −0.369
Gender 0.079 1.790 0.185 2–5 years −0.369
Male −0.961 >5 years 2.708
Female 1.041 Satisfaction of wearing −0.540 26.083 0.001
Age (years) −0.311 8.619 0.001 prosthetic eyes
16–25 −1.565 Uncomfortable −2.119
26–55 0.404 General comfortable −0.192
0.423 Very comfortable 1.363
0.423
2.448
2.448 correlated with depressive and anxiety symptoms. Patients’
>55 2.607 satisfaction is associated with both the ocular prosthesis
Geographical area of residence 0.107 1.742 0.191 itself and the individuals’ usage experiences. Adverse
Rural 0.750 reactions, such as eye secretions and inflammation, can
Urban −1.333 significantly affect the comfort of wearing prostheses and
Education status -0.162 1.957 0.166 lead to depressive and anxiety problems. Moreover, the
feelings of discomfort and perceived discrimination during
Junior high or below −0.905 social interactions may also influence patient satisfaction
Senior high school 1.106 and psychological well-being. 7,25
University or above 1.106 In summary, depressive and anxiety symptoms are
Marital status 0.056 0.608 0.438
still prevalent among patients with ocular prostheses.
Married 1.200 Understanding the associated factors, particularly those
Non-married −0.834 associated with ocular prosthesis wearing, can help us
Economic status −0.099 0.784 0.460 identify high-risk patients. Long-term comprehensive
Low −0.860 care is essential for the successful social and psychological
Middle −0.048 rehabilitation of these patients to mitigate their depression
Upper middle −0.048 and anxiety.
High 3.424 Several strengths of this study should be acknowledged.
Enucleated eye 0.023 0.218 0.642 First, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that
Left −1.106 systematically investigates the impact of ocular prosthesis-
Right 0.905 related factors, including the cause of wearing and the
materials used to make the prostheses, on depressive and
Cause of anophthalmos 0.128 3.740 0.014 anxiety symptoms. In addition, on top of the optimal
Congenital malformation −0.222 scale regression model, standardized psychological
Trauma 2.699 measurement was conducted, yielding results that are more
Tumor 0.015 objective and compelling compared to previous studies.
Others −1.056 This study is not without limitations. First, some
Materials of prosthetic eyes 0.124 4.963 0.001 factors, such as the appearance of the ocular prosthesis,
Hydroxyapatite −0.132 were not investigated in this study. These factors should
Medpor −0.634 be taken into consideration in future research. Second,
Alumina −3.965 all participants recruited in this study were the users of
Autologous issue −1.630 the Haodaifu platform. Therefore, the generalizability of
None 1.624 this study’s findings is limited and less convincing. Third,
Time of wearing prosthetic eyes 0.080 0.221 0.640 psychological symptoms were evaluated using a self-
rated scale, which may lead to self-report bias. Fourth,
<6 months −0.369 the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 could only measure the general
6 months–1 year −0.369 depressive and anxiety symptoms rather than the exact
(Cont’d...) symptoms caused by ocular prosthesis wearing, which may
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.1761