Page 55 - JCTR-10-1
P. 55
Gonda et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(1): 33-51 51
Supplementary Data 6
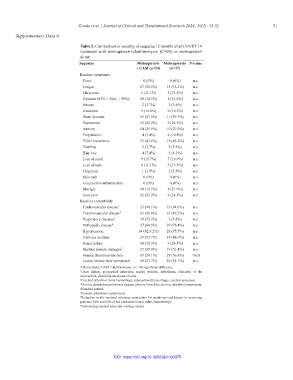
Table 5. Comparison of severity of sequelae 12 months after COVID-19
treatment with molnupiravir+clarithromycin (CAM) or molnupiravir
alone
Sequelae Molnupiravir Molnupiravir P‑value
+ CAM (n=54) (n=37)
Baseline symptoms
Fever 0 (0%) 0 (0%) n.s.
Fatigue 17 (31.5%) 13 (35.1%) n.s.
Chest pain 6 (11.1%) 5 (13.5%) n.s.
Dyspnea (93% < SpO < 96%) 10 (18.5%) 8 (21.6%) n.s.
2
Nausea 2 (3.7%) 2 (5.4%) n.s.
Headache 8 (14.8%) 6 (16.2%) n.s.
Sleep disorder 15 (27.8%) 11 (29.7%) n.s.
Depression 12 (22.2%) 9 (24.3%) n.s.
Anxiety 14 (25.9%) 10 (27.0%) n.s.
Palpitations 4 (7.4%) 4 (10.8%) n.s.
Effort intolerance 23 (42.6%) 16 (43.2%) n.s.
Diarrhea 2 (3.7%) 2 (5.4%) n.s.
Hair loss 4 (7.4%) 3 (8.1%) n.s.
Loss of smell 9 (16.7%) 7 (18.9%) n.s.
Loss of taste 6 (11.1%) 5 (13.5%) n.s.
Cingulum 1 (1.9%) 2 (5.4%) n.s.
Skin rash 0 (0%) 0 (0%) n.s.
Conjunctiva inflammation 0 (0%) 0 (0%) n.s.
Myalgia 10 (18.5%) 8 (21.6%) n.s.
Joint pain 12 (22.2%) 9 (24.3%) n.s.
Baseline comorbidity
Cardiovascular disease 1 53 (98.1%) 35 (94.6%) n.s.
Cerebrovascular disease 2 43 (80.0%) 33 (89.2%) n.s.
Respiratory diseases 3 39 (72.2%) 2 (5.4%) n.s.
Orthopedic disease 4 37 (68.5%) 29 (78.4%) n.s.
Hypertension 34 (62.9.2%) 28 (75.7%) n.s.
Diabetes mellitus 29 (53.7%) 18 (48.6%) n.s.
Renal failure 10 (18.5%) 9 (24.3%) n.s.
Skeletal muscle damages 5 27 (50.0%) 19 (51.4%) n.s.
Venous thromboembolism 13 (24.1%) 21 (56.8%) <0.05
Lower urinary tract symptoms 6 29 (53.7%) 20 (54.1%) n.s.
Abbreviations: CAM: Clarithromycin; n.s.: No significant difference.
1 Heart failure, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, arrhythmia, dilatation of the
myocarditis, dissecting aneurysm of aorta.
2 Cerebral infarction, brain hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, cerebral aneurysm.
3 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic bronchitis, chronic interstitial pneumonia,
bronchial asthma.
4 Fracture, prosthesis replacement.
5 Reduction in the maximal voluntary contraction for quadriceps and biceps in recovering
patients (54% and 69% of the predicted normal value, respectively).
6 Postvoiding residual urine and voiding volume
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.00075