Page 86 - MSAM-2-4
P. 86
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Laser DED-produced Ti-6Mn-4Mo alloy
A
B C
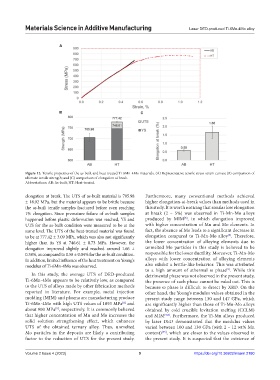
Figure 12. Tensile properties of the as-built and heat-treated Ti-6Mn-4Mo materials. (A) Representative tensile stress-strain curves; (B) comparison of
ultimate tensile strength; and (C) comparison of elongation at break.
Abbreviations: AB: As-built; HT: Heat-treated.
elongation at break. The UTS of as-built material is 705.98 Furthermore, many conventional methods achieved
± 18.92 MPa, but the material appears to be brittle because higher elongation-at-break values than methods used in
the as-built tensile samples fractured before even reaching this study. It is worth noticing that similar low elongation
1% elongation. Since premature failure of as-built samples at break (2 – 5%) was observed in Ti-Mn-Mo alloys
[8]
happened before plastic deformation was reached, YS and produced by MIM , in which elongation improved
UTS for the as-built condition were measured to be at the with higher concentration of Mn and Mo elements. In
same level. The UTS of the heat-treated material was found fact, the absence of Mo leads to a significant decrease in
[9]
to be at 777.42 ± 3.09 MPa, which was also not significantly elongation compared to Ti-Mn-Mo alloy . Therefore,
higher than its YS at 746.61 ± 0.73 MPa. However, the the lower concentration of alloying elements due to
elongation improved slightly and reached around 1.66 ± unmelted Mo particles in this study is believed to be
0.38%, as compared to 0.58 ± 0.04% for the as-built condition. responsible for the lower ductility. Moreover, Ti-Mn-Mo
In addition, limited influence of the heat treatment on Young’s alloys with lower concentration of alloying elements
modulus of Ti-6Mn-4Mo was observed. also exhibit a brittle-like behavior. This was attributed
to a high amount of athermal ω phase . While this
[5]
In this study, the average UTS of DED-produced detrimental phase was not observed in the present study,
Ti-6Mn-4Mo appears to be relatively low, as compared the presence of such phase cannot be ruled out. This is
to the UTS of alloys made by other fabrication methods because ω phase is difficult to detect by XRD. On the
reported in literature. For example, metal injection other hand, the Young’s modulus values obtained in the
molding (MIM) and plasma arc manufacturing produce present study range between 130 and 147 GPa, which
Ti-6Mn-4Mo with high UTS values of 1093 MPa and are significantly higher than those of Ti-Mn-Mo alloys
[8]
about 900 MPa , respectively. It is commonly believed obtained by cold crucible levitation melting (CCLM)
[9]
that higher concentration of Mn and Mo increases the and MIM [5,8] . Furthermore, the Ti-Mn alloys produced
solid solution strengthening effect, which enhances by laser DED demonstrated that the modulus values
UTS of the obtained ternary alloy. Thus, unmelted varied between 100 and 130 GPa (with 2 – 12 wt% Mn
Mo particles in the deposits are likely a contributing content) [35] , which are closer to the values observed in
factor to the reduction of UTS for the present study. the present study. It is suspected that the existence of
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2180