Page 108 - OR-1-3
P. 108
A B C
D
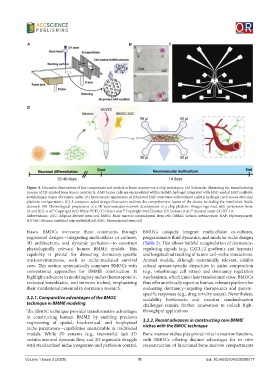
Figure 4. Schematic illustrations of key components and models in bone marrow-on-a-chip techniques. (A) Schematic illustrating the manufacturing
process of 3D-printed bone tumor constructs. A549 tumor cells are encapsulated within GelMA hydrogel integrated with MSC-seeded HAP scaffolds,
establishing a tumor dormancy niche. (B) Macroscopic appearance of fabricated HAP structures with/without GelMA hydrogel (red) across dual chip
platform configurations. (C) A computer-aided design illustration outlines the comprehensive layout of the device, including the interlinked fluidic
channels. (D) Chronological progression of a 3D neurovascular network development in a chip platform. Images reprinted with permission from:
(A and B) Ji et al. Copyright 2023 Wiley-VCH; (C) Glaser et al. Copyright 2022 Elsevier; (D) Isosaari et al., licensed under CC-BY 4.0.
69
71
67
Abbreviations: ASC: Adipose-derived stem cell; BMSC: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell; GelMA: Gelatin methacrylate; HAP: Hydroxyapatite;
HUVEC: Human umbilical vein epithelial cell; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.
biases. BMOCs overcome these constraints through BMOCs uniquely integrate multicellular co-cultures,
engineered designs—integrating multicellular co-cultures, programmable fluid dynamics, and modular niche designs
3D architectures, and dynamic perfusion—to construct (Table 2). This allows faithful recapitulation of dormancy-
physiologically relevant human BMME models. This regulating signals (e.g., CXCL12 gradients and hypoxia)
capability is pivotal for dissecting dormancy-specific and longitudinal tracking of tumor cell–niche interactions.
microenvironments, such as niche-mediated survival Animal models, although systemically relevant, exhibit
cues. This section systematically compares BMOCs with critical species-specific disparities in niche composition
conventional approaches for BMME construction. It (e.g., osteolineage cell ratios) and dormancy regulation
highlights advances in modeling key niches (hematopoietic, mechanisms, which limit their translational value. BMOCs
endosteal/osteoblastic, and immune niches), emphasizing thus offer an ethically superior, human-relevant platform for
their translational potential in dormancy research. evaluating dormancy-targeting therapeutics and patient-
specific responses (e.g., drug toxicity assays). Nevertheless,
3.2.1. Comparative advantages of the BMOC scalability bottlenecks and vascular standardization
technique in BMME modeling challenges require further innovation to unlock high-
The BMOC technique provides transformative advantages throughput applications.
in constructing human BMME by enabling precision
engineering of spatial, biochemical, and biophysical 3.2.2. Recent advances in constructing core BMME
niche parameters—capabilities unattainable in traditional niches with the BMOC technique
models. While 2D systems (e.g., transwells) lack 3D Bone marrow niches play pivotal roles in marrow function,
architecture and dynamic flow, and 3D organoids struggle with BMOCs offering distinct advantages for in vitro
with standardized niche integration and perfusion control, reconstruction of functional bone marrow compartments
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2025) 11 doi: 10.36922/OR025200017