Page 106 - ESAM-1-2
P. 106
Engineering Science in
Additive Manufacturing HIP temperature effects on LPBF Hastelloy X
was measured using Qness Q10 hardness tester (Qness, completely disappeared at HIP1180 and HIP1210. The fine
Austria), with a test load of 1 kg and a holding time of 10 s. and coarse equiaxed grains were distributed at the edge and
Eight points were sampled along the central line in the the center of the scanning tracks at HIP1100, respectively,
building direction of each specimen. According to the GB/T as shown in Figure 2B. An uneven distribution of grain size
228.1-2010 standard, tensile tests at room temperature was observed at HIP1180, as shown in Figure 2C. The finer
were conducted using the UTM5105X electronic universal equiaxed grains were engulfed by larger ones at HIP1210,
material testing machine manufactured by SUNS (China). resulting in a more uniform grain size distribution, as
The tensile speed was set at 0.5 mm/min before yielding depicted in Figure 2D.
and 2.5 mm/min after yielding. The tensile test specimens Figure 3 shows the EBSD results of the as-built,
were obtained by wire electrical discharge machining, and HIP1100, HIP1180, and HIP1210 specimens to investigate
the dimensions of the tensile test specimens are shown in the microstructural evolution after various HIP
Figure 1B. Before the tensile test, the surfaces were polished treatments. The columnar grains in the as-built specimen
to reduce the influence of surface roughness on the tensile were characterized by a small aspect ratio, with a length
properties.
of 80 – 100 μm, corresponding to the set laser scanning
Based on the average actual service temperature of spacing, as shown in Figure 3A . In addition, the grains
1
hot-end components of aerospace engines manufacturing, were observed with a maximum multiple of uniform
high-temperature tensile tests at 900°C were conducted density (MUD) value of 6.4, as depicted in Figure 3A .
3
to investigate the effect of HIP temperature on high- After the HIP1100 treatment, the columnar grains of
temperature mechanical properties according to the GB/T the as-built specimen transformed into equiaxed grains
37783-2019 standard. The tests were performed using the without a specific grain orientation, accompanied by a MUD
SANS-CMT-52052 electronic universal testing machine value of 4.834, as shown in Figure 3B and B . At HIP1180
1
3
(MTS Systems Corporation, China), with a tensile speed of and HIP1210, the MUD values decreased to 2.915 and 3.487,
0.5 mm/min before yielding and 1.5 mm/min after yielding. respectively, indicating that the texture in the as-built specimen
was almost eliminated, as depicted in Figure 3C , C , D , and D .
3. Results and discussion Therefore, it could be inferred that as the HIP temperature
1
1
3
3
3.1. Microstructures increased, a random grain orientation was achieved and the
microstructure anisotropy was restrained.
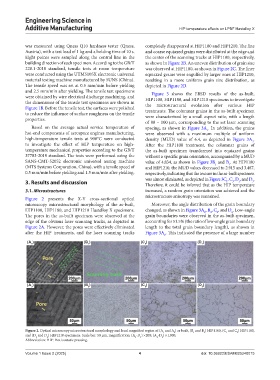
Figure 2 presents the X-Y cross-sectional optical
microscopy microstructural morphology of the as-built, Moreover, the angle distribution of the grain boundary
HIP1100, HIP1180, and HIP1210 Hastelloy X specimens. changed, as shown in Figure 3A , B , C , and D . Low-angle
2
2
2
2
The pores in the as-built specimen were observed at the grain boundaries were observed in the as-built specimen,
edge of the obvious laser scanning tracks, as depicted in accounting for 51.5% (the ratio of low-angle grain boundary
Figure 2A. However, the pores were effectively eliminated length to the total grain boundary length), as shown in
after the HIP treatments, and the laser scanning tracks Figure 3A . This indicated the presence of a large number
2
(A ) (B ) (C ) (D )
1 1 1 1
(A ) (B ) (C ) (D )
2 2 2 2
Figure 2. Optical microscopy microstructural morphology and local magnified region of (A and A ) as built, (B and B ) HIP1100, (C and C ) HIP1180,
2
1
2
1
1
2
and (D and D ) HIP1210 specimens. Scale bar: 50 μm, magnification: (A -D ) ×200; (A -D ) ×1,000.
2
1
1
2
2
1
Abbreviation: HIP: Hot isostatic pressing.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/ESAM025240015