Page 72 - GTM-4-3
P. 72
Global Translational Medicine Precision medicine via personalized nutrition
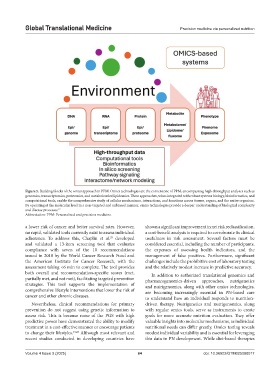
Figure 5. Building blocks of the omics approach in PPM. Omics technologies are the cornerstone of PPM, encompassing high-throughput analyses such as
genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics/lipidomics. These approaches, when integrated with robust systems biology, bioinformatics, and
computational tools, enable the comprehensive study of cellular mechanisms, interactions, and functions across tissues, organs, and the entire organism.
By operating at the molecular level in a non-targeted and unbiased manner, omics technologies provide a deeper understanding of biological complexity
and disease processes. 17
Abbreviation: PPM: Personalized and precision medicine.
a lower risk of cancer and better survival rates. However, shown a significant improvement in net risk reclassification,
no rapid, validated tools currently exist to assess individual a cost-benefit analysis is required to corroborate its clinical
adherence. To address this, Chaplin et al. developed usefulness in risk assessment. Several factors must be
25
and validated a 13-item screening tool that evaluates considered essential, including the number of participants,
compliance with seven of the 10 recommendations the expenses of assessing health indicators, and the
issued in 2018 by the World Cancer Research Fund and management of false positives. Furthermore, significant
the American Institute for Cancer Research, with the challenges include the prohibitive cost of laboratory testing
assessment taking <6 min to complete. The tool provides and the relatively modest increase in predictive accuracy.
both overall and recommendation-specific scores (met, In addition to authorized translational genomics and
partially met, and not met), facilitating targeted prevention pharmacogenomics-driven approaches, nutrigenetics
strategies. This tool supports the implementation of and nutrigenomics, along with other omics technologies,
comprehensive lifestyle interventions that lower the risk of are becoming increasingly essential in PN-based care
cancer and other chronic diseases. to understand how an individual responds to nutrition-
Nevertheless, clinical recommendations for primary driven therapy. Nutrigenetics and nutrigenomics, along
prevention do not suggest using genetic information to with regular omics tools, serve as instruments to create
assess risk. This is because none of the PGS with high goals for more accurate nutrition evaluation. They offer
predictive power have demonstrated the ability to modify valuable insights into molecular mechanisms, as individual
treatment in a cost-effective manner or encourage patients nutritional needs can differ greatly. Omics testing reveals
to change their lifestyles. 15,23 Although most relevant and modest individual variability and is essential for leveraging
recent studies conducted in developing countries have this data in PN development. While diet-based therapies
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 64 doi: 10.36922/GTM025080017