Page 73 - GTM-4-3
P. 73
Global Translational Medicine Precision medicine via personalized nutrition
are used for various clinical conditions, such as inborn
errors of metabolism, progress in expanding omics data
has been limited. This hampers a deeper mechanistic
understanding of cellular networks influenced by nutrition-
driven gene expression and complete gene regulation. The
main challenge lies in the clinical sector, which should
integrate existing data, overcome the limitations of self-
reported procedures in research, and make omics data,
along with nutrigenetics and nutrigenomics research,
widely accessible. 20,26-29
We have only recently started to recognize specific
gene–diet connections, as many clinical and molecular
phenotypes, such as body mass index, are influenced
by multiple genes. While nutrigenetics focuses on how
genetic variations impact metabolism, nutrigenomics
examines how nutrients (food compounds) affect gene
Figure 6. Multiomics data encompass information from various
omics disciplines, including genomics, epigenomics, transcriptomics, activity, assessing how mutations affect the assimilation
proteomics, metabolomics, and phenomics. These data are derived of metabolites. Recent advancements in genomics and
from diverse assays and experiments, spanning multiple spatial and PPM have led to a growing number of evidence-based
temporal scales. While genomics has traditionally been a primary applications with the potential to significantly reduce
focus in personalized and precision medicine, other omics fields are
increasingly contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of how morbidity and mortality in millions of individuals.
an individual’s complex biology influences their health. High-throughput In summary, it is important to note that, in contrast
multiomics technologies enable the collection of extensive and holistic to general genomics-related achievements, nutritional
biological data, whereas advanced computational tools facilitate high-
dimensional data modeling, making analysis accessible and user- genomics is still in its early stages compared with PPM.
friendly. 18 However, using genomics indicators and other clinical
tools represents a practical application of this emerging
technology. Meanwhile, advancements in genomics
have led to the concept that a deeper understanding of
individual characteristics, such as genotype, can enable
more precise personalization of pharmaceutical and
nutritional therapies. PN is customized based on an
individual’s specific genetic profile, lifestyle, and health
objectives, in contrast to general dietary guidelines that
offer broad recommendations for the population as a
whole (Figure 8).
30
It is crucial to recognize that current PN approaches
have achieved only limited scientific success in improving
dietary habits or addressing diet-related health conditions.
These strategies often target narrow population subgroups,
limiting their broader impact on public health. To
overcome this, a more holistic approach is needed—one
that integrates biomedical and dietary assessments with
psychobehavioral insights and innovative digital and
diagnostic technologies for comprehensive data collection.
An adaptive PN counseling system addresses this need
by combining biomedical and health phenotyping, stable
and dynamic behavioral indicators, and contextual food
environment data. This integration utilizes advanced
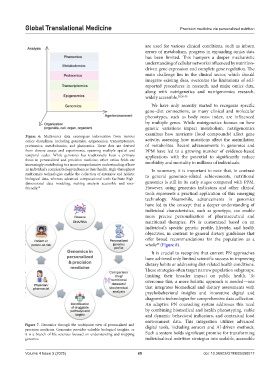
Figure 7. Genomics through the multipoint view of personalized and digital tools, including sensors and AI-driven methods.
precision medicine. Genomics provides valuable biological insights, as
it is a branch of life sciences focused on understanding and mapping Such a system holds significant promise for transforming
genomes. individualized nutrition strategies into scalable, accessible
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 65 doi: 10.36922/GTM025080017