Page 559 - IJB-10-2
P. 559
International Journal of Bioprinting OLS design for distal femur osseointegration
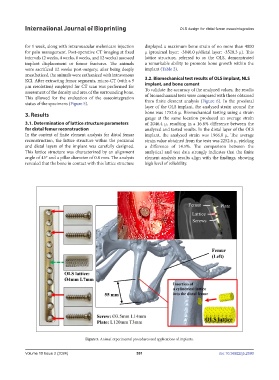
for 1 week, along with intramuscular meloxicam injection displayed a maximum bone strain of no more than 4000
for pain management. Post-operative CT imaging at fixed μ (proximal layer: -3840.0 μ/distal layer: -3528.3 μ). This
intervals (2 weeks, 4 weeks, 8 weeks, and 12 weeks) assessed lattice structure, referred to as the OLS, demonstrated
implant displacement or femur fractures. The animals a remarkable ability to promote bone growth within the
were sacrificed 12 weeks post-surgery; after being deeply implant (Table 2).
anesthetized, the animals were euthanized with intravenous
KCl. After extracting femur segments, micro-CT (with a 9 3.2. Biomechanical test results of OLS implant, NLS
µm resolution) employed for CT scan was performed for implant, and bone cement
assessment of the density and area of the surrounding bone. To validate the accuracy of the analyzed values, the results
This allowed for the evaluation of the osseointegration of biomechanical tests were compared with those obtained
status of the specimens (Figure 5). from finite element analysis (Figure 6). In the proximal
layer of the OLS implant, the analyzed strain around the
3. Results bone was 1752.6 μ. Biomechanical testing using a strain
gauge at the same location produced an average strain
3.1. Determination of lattice structure parameters of 2046.4 μ, resulting in a 16.8% difference between the
for distal femur reconstruction analyzed and tested results. In the distal layer of the OLS
In the context of finite element analysis for distal femur implant, the analyzed strain was 1966.8 μ. The average
reconstruction, the lattice structure within the proximal strain value obtained from the tests was 2252.6 μ, yielding
and distal layers of the implant was carefully designed. a difference of 14.5%. The comparison between the
This lattice structure was characterized by an alignment analytical and test data strongly indicates that the finite
angle of 45° and a pillar diameter of 0.8 mm. The analysis element analysis results align with the findings, showing
revealed that the bone in contact with this lattice structure high level of reliability.
Figure 5. Animal experimental procedures and applications of implants.
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 551 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2590