Page 564 - IJB-10-2
P. 564
International Journal of Bioprinting OLS design for distal femur osseointegration
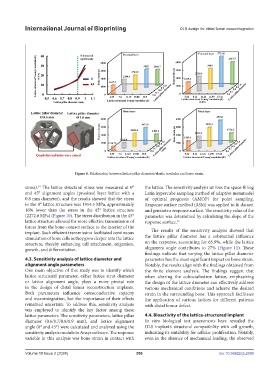
Figure 8. Relationship between lattice pillar diameter/elastic modulus and bone strain.
54
stress). The lattice structural stress was measured at 0° the lattice. The sensitivity analysis utilizes the space-filling
and 45° alignment angles (proximal layer lattice with a Latin hypercube sampling method of adaptive metamodel
0.8 mm diameter), and the results showed that the stress of optimal prognosis (AMOP) for point sampling.
in the 0° lattice structure was 1954.5 MPa, approximately Response surface method (RSM) was applied to fit dataset
16% lower than the stress in the 45° lattice structure and generate a response surface. The sensitivity value of the
(2272.8 MPa) (Figure 10). The stress distribution in the 45° parameter was determined by calculating the slope of the
lattice structure allowed for more effective transmission of response surface. 55
forces from the bone-contact surface to the interior of the
implant. Such efficient transmission facilitated continuous The results of the sensitivity analysis showed that
stimulation of bone cells as they grew deeper into the lattice the lattice pillar diameter has a substantial influence
structure, thereby enhancing cell attachment, migration, on the response, accounting for 65.9%, while the lattice
growth, and differentiation. alignment angle contributes to 27% (Figure 11). These
findings indicate that varying the lattice pillar diameter
4.3. Sensitivity analysis of lattice diameter and parameter has the most significant impact on bone strain.
alignment angle parameters Notably, the results align with the findings obtained from
One main objective of this study was to identify which the finite element analysis. The findings suggest that
lattice structural parameter, either lattice strut diameter when altering the cuboctahedron lattice, emphasizing
or lattice alignment angle, plays a more pivotal role the design of the lattice diameter can effectively address
in the design of distal femur reconstruction implants. various mechanical conditions and achieve the desired
Both parameters influence osteoconductive capacity strain in the surrounding bone. This approach facilitates
and osseointegration, but the importance of their effects the application of various lattices for different patients
remained uncertain. To address this, sensitivity analysis with distal femur defect.
was employed to identify the key factor among these
lattice parameters. The sensitivity parameters, lattice pillar 4.4. Bioactivity of the lattice-structured implant
diameter (0.6/0.7/0.8/0.9 mm), and lattice alignment In vitro biological test assessments have revealed the
angle (0° and 45°) were calculated and analyzed using the OLS implant’s structural compatibility with cell growth,
sensitivity analysis module in Ansys software. The response indicating its suitability for cellular proliferation. Notably,
variable in this analysis was bone strain in contact with even in the absence of mechanical loading, the observed
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 556 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2590