Page 99 - IJB-10-4
P. 99
International Journal of Bioprinting Biomaterials with antibacterial agents
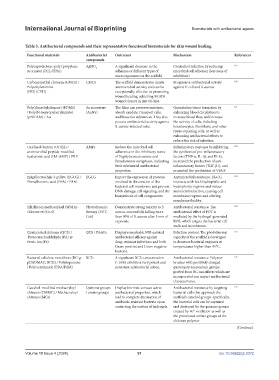
Table 3. Antibacterial compounds and their representative functional biomaterials for skin wound healing.
Functional materials Antibacterial Outcomes Mechanism References
compounds
Polycaprolactone-poly (propylene AgNO 3 A significant decrease in the Controlled infection by reducing 119
succinate) (PCL-PPSu) adhesion of different types of microbial cell adhesion (less zone of
microorganisms on the scaffold inhibition)
Carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCS) / CMCS The scaffold demonstrates innate Progressive antibacterial activity 120
Polyethylenimine antimicrobial activity and can be against E. coli and S. aureus
(PEI) (CPH) exceptionally effective in promoting
wound healing, achieving 98.02%
wound closure in just 14 days.
Poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) Au nanostars The films can preserve moisture, Granulation tissue formation by 121
/ Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (AuNS) absorb exudate, transport cells, enhancing blood circulation to
(pNIPAM) / Au and bioactive substances. They also increase blood flow, and increase
possess antibacterial activity against the activity of cells, including
S. aureus-infected mice. keratinocytes, fibroblasts, and other
tissue-repairing cells, as well as
enhancing antibacterial effects to
reduce the risk of infection
Oxidized dextran (ODEX) / AMPs Reduce the microbial cell Inflammatory response by inhibiting 122
antimicrobial peptide-modified adherence in the inhibitory zones the synthesis of pro-inflammatory
hyaluronic acid (HA-AMP) / PRP of Staphylococcus aureus and factors (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6),
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, indicating increased the production of anti-
their substantial antibacterial inflammatory factors (TGF-β1), and
properties. promoted the production of VEGF
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) / EGCG Impact the expression of proteins Antimicrobial resistance. EGCG 123
Phenylboronic acid (PBA) / PAM involved in the creation of the interacts with both hydrophilic and
bacterial cell membrane and prevent hydrophobic regions and induce
DNA damage, cell signaling, and the antimicrobial action, causing cell
biosynthesis of cell components. membrane rupture and altering
membrane fluidity.
Silk fibroin methacryloyl (SFMA)- Photodynamic Demonstrate strong toxicity to S. Antibacterial resistance. The 124
chlorine e6 (Ce-6) therapy (PDT; aureus, successfully killing more antibacterial effect of PDT is
Ce6) than 90% of S. aureus after 5 min of mediated by the hydrogel-generated
exposure. ROS, which targets the bacterial cell
walls and membranes.
Quaternized chitosan (QCS) / QCS / PA@Fe Display remarkable NIR-assisted Infection control. The photothermal 125
Protocatechualdehyde (PA) @ antibacterial efficacy against capacity of the scaffold is leveraged
Ferric ion (Fe) drug-resistant infections and both to denature bacterial enzymes at
Gram-positive and Gram-negative temperatures higher than 45°C.
bacteria.
Bacterial cellulose nanofibers (BC-g- BCD A significant BCD concentration Antibacterial resistance. Polymer 126
pDADMAC, BCD) / Polydopamine (>10%) exhibits a very potent and brushes with positively charged
/ Poly acrylamide (PDA/PAM) persistent antibacterial action. quaternary ammonium groups
grafted from BC nanofibers which are
incorporated can impart antibacterial
characteristics.
Catechol-modified methacryloyl Quinone groups Display intrinsic contact-active Antibacterial resistance by targeting 127
chitosan (CMMC) / Methacryloyl / amino groups antibacterial properties, which bacterial cells that approach the
chitosan (MCs) lead to complete decimation of scaffold’s catechol groups. specifically,
antibiotic-resistant bacteria upon the bacterial cells can be captured
contacting the surface of hydrogels. and destroyed by the quinone groups
created by Fe oxidation as well as
3+
the protonated amino groups of the
chitosan polymer
(Continue)
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 91 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3372