Page 33 - IJB-7-3
P. 33
Ren, et al
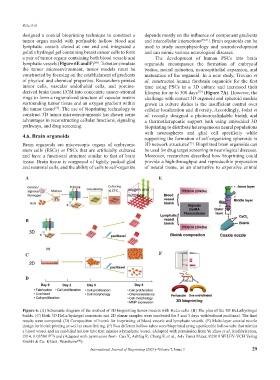
designed a coaxial bioprinting technique to construct a depends mostly on the influence of component gradients
tumor organ model with perfusable hollow blood and and intercellular interactions [70,71] . Brain organoids can be
lymphatic vessels closed at one end and integrated a used to study neurophysiology and neurodevelopment
gelatin hydrogel gel containing breast cancer cells to form and can mimic various neurological diseases.
a pair of tumor organs containing both blood vessels and The development of human PSCs into brain
lymphatic vessels (Figure 6E and F) . To better simulate organoids encompasses the formation of embryoid
[68]
the tumor microenvironment, tumor models must be bodies, neural induction, neuroepithelial expansion, and
constructed by focusing on the establishment of gradients maturation of the organoid. In a new study, Trevino et
of physical and chemical properties. Researchers printed al. constructed human forebrain organoids for the first
tumor cells, vascular endothelial cells, and porcine- time using PSCs in a 3D culture and increased their
derived brain tissue ECM into concentric cancer-stromal lifespan for up to 300 days (Figure 7A). However, the
[72]
rings to form a regionalized structure of vascular matrix challenge with current 3D organoid and spheroid models
surrounding tumor tissue and an oxygen gradient within grown in culture dishes is the insufficient control over
the tumor tissue . The use of bioprinting technology to cellular localization and diversity. Accordingly, Jodat et
[69]
construct 3D tumor microenvironments has shown some al. recently designed a photocrosslinkable bioink and
advantages in reconstructing cellular functions, signaling a thermotherapeutic support bath using embedded 3D
pathways, and drug screening. bioprinting to distribute heterogeneous neural populations
with neurospheres and glial cell specificity while
4.6. Brain organoids supporting the formation of self-organizing spheroids in
Brain organoids are microscopic organs of embryonic 3D network structures . Bioprinted brain organoids can
[73]
stem cells (ESCs) or PSCs that are artificially cultured be used for drug target screening in neurological diseases.
and have a functional structure similar to that of brain Moreover, researchers described how bioprinting could
tissue. Brain tissue is composed of tightly packed glial provide a high-throughput and reproducible preparation
and neuronal cells, and the ability of cells to self-organize of neural tissue, as an alternative to expensive animal
A E
B
C F
D
Figure 6. (A) Schematic diagram of the method of 3D bioprinting tumor models with HeLa cells. (B) The plan of the 3D HeLa/hydrogel
builds. (C) Both 3D HeLa/hydrogel constructs and 2D planar samples were incubated for 5 and 3 days with/without paclitaxel. The final
results were compared. (D) Composition of bioink for bioprinting of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. (E) Multi-layer coaxial nozzle
design for bioink printing as well as cross-linking. (F) Two different hollow tubes were bioprinted using a perfusable hollow tube that mimics
a blood vessel and an end-blind hollow tube that mimics a lymphatic vessel. (Adapted with permission from Yu Zhao et al, Biofabrication,
2014, 6 035001 ) and (Adapted with permission from Cao X, Ashfaq R, Cheng F, et al., Adv Funct Mater, ©2019 WILEY‐VCH Verlag
[67]
GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim ).
[68]
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 3 29