Page 220 - IJB-8-1
P. 220
Nano-Hydroxyapatite Bone Scaffolds with Different Porous Structures Processed by Digital Light Processing 3D Printing
A
B
C
D
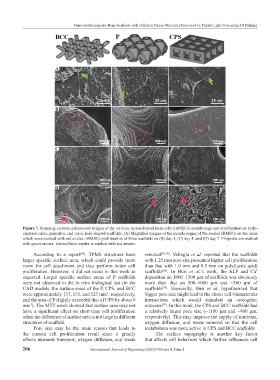
Figure 7. Scanning electron microscopy images of the rat bone mesenchymal stem cells (rBMSCs) morphology and proliferation on body-
centered cubic, primitive, and cubic pore-shaped scaffolds. (A) Magnified images of the morphologies of the seeded rBMSCs on the areas
which were marked with red circles. rBMSCs proliferation of three scaffolds on (B) day 1, (C) day 4, and (D) day 7. Filopodia are marked
with green arrows. Extracellular matrix is marked with red arrows.
According to a report , TPMS structures have removal [38,59] . Velioglu et al. reported that the scaffolds
[58]
larger specific surface area, which could provide more with 1.25 mm pore size presented higher cell proliferation
room for cell attachment and thus perform better cell than that with 1.0 mm and 0.5 mm on poly(lactic acid)
proliferation. However, it did not occur in this work as scaffolds . In Huri et al.’s work, the ALP and Ca
[40]
+
expected. Larger specific surface areas of P scaffolds deposition on 1000–1500 µm of scaffolds was obviously
were not observed in the in vitro biological test (in the more than that on 500–1000 µm and <500 µm of
CAD models, the surface areas of the P, CPS, and BCC scaffolds . Especially, Huri et al. hypothesized that
[39]
were approximately 157, 151, and 127 mm , respectively, bigger pore size might lead to the closer cell-biomaterials
3
and the area of P slightly exceeded that of CPS by about 6 interactions which would stimulate an osteogenic
mm ). The MTT result showed that surface area may not outcome . In this work, the CPS and BCC scaffolds had
3
[39]
have a significant effect on short-time cell proliferation a relatively larger pore size (~1180 µm and ~900 µm,
when the difference of surface area is not large in different respectively). This may improve the supply of nutrients,
structures of scaffold. oxygen diffusion, and waste removal so that the cell
Pore size may be the main reason that leads to metabolism was more active in CPS and BCC scaffolds.
the current cell proliferation result since it greatly The surface topography is another key factor
affects nutrients transport, oxygen diffusion, and waste that affects cell behaviors which further influences cell
206 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 1