Page 196 - IJB-9-2
P. 196
International Journal of Bioprinting A regulated GelMA-MSCs scaffold by three-dimensional bioprinting
A
B C D
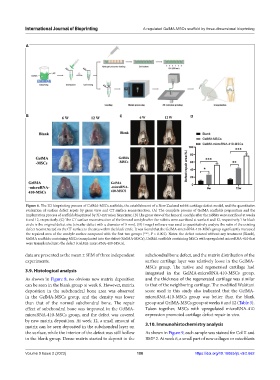
Figure 6. The 3D bioprinting process of GelMA-MSCs scaffolds, the establishment of a New Zealand rabbit cartilage defect model, and the quantitative
evaluation of surface defect repair by gross view and CT surface reconstruction. (A) The complete process of GelMA scaffolds preparation and the
implantation process of scaffolds bioprinted by 3D extrusion bioprinter. (B) The gross view of the femoral condyle after the rabbits were sacrificed at weeks
6 and 12, respectively. (C) The CT surface reconstruction of the femoral condyle after the rabbits were sacrificed at weeks 6 and 12, respectively. The black
circle is the original defect size (circular defect with a diameter of 5 mm). (D) ImageJ software was used to quantitatively analyze the ratio of the existing
defect reconstructed on the CT surface to the area within the black circle. It was found that the GelMA-microRNA-410-MSCs group significantly increased
the repaired area of the condyle surface compared with the first two groups (***, P < 0.001). Notes: the defect sutured without any treatment (Blank),
GelMA scaffolds containing MSCs transplanted into the defect (GelMA-MSCs), GelMA scaffolds containing MSCs with upregulated microRNA-410 that
were transplanted into the defect (GelMA-microRNA-410-MSCs).
data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent subchondral bone defect, and the matrix distribution of the
experiments. surface cartilage layer was relatively loose in the GelMA-
MSCs group. The native and regenerated cartilage had
3.9. Histological analysis integrated in the GelMA-microRNA-410-MSCs group,
As shown in Figure 8, no obvious new matrix deposition and the thickness of the regenerated cartilage was similar
can be seen in the blank group at week 6. However, matrix to that of the neighboring cartilage. The modified Wakitani
deposition in the subchondral bone area was observed score used in this study also indicated that the GelMA-
in the GelMA-MSCs group, and the density was lower microRNA-410-MSCs group was better than the blank
than that of the normal subchondral bone. The repair group and GelMA-MSCs group at weeks 6 and 12 (Table 3).
effect of subchondral bone was improved in the GelMA- Taken together, MSCs with upregulated microRNA-410
microRNA-410-MSCs group, and the defect was covered expression promoted cartilage defect repair in vivo.
by new matrix deposition. At week 12, a small amount of
matrix can be seen deposited in the subchondral layer on 3.10. Immunohistochemistry analysis
the surface, while the interior of the defect was still hollow As shown in Figure 9, each sample was stained for Col II and
in the blank group. Dense matrix started to deposit in the BMP 2. At week 6, a small part of new collagen or osteoblasts
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 188 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.662