Page 202 - IJB-9-3
P. 202
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed vascularized biofunctional scaffold
Figure 6. Effect of hydrogels on macrophage polarization in vitro. (A, B) Results of qPCR of M1-related gene expression (CCR7 and iNOS) (n = 3/group).
(C, D) Results of qPCR of M2-related gene expression (CD206 and Arg1) (n = 3/group). (E) Immunofluorescence staining of iNOS in RAW264.7 cells
cultured on each group of hydrogels. (F) Immunofluorescence staining of Arg1 in RAW264.7 cells cultured on each group of hydrogels. All experiments
were replicated three times. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
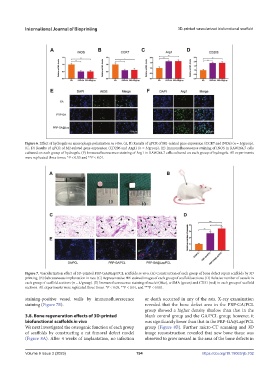
Figure 7. Vascularization effect of 3D-printed PRP-GA@Lap/PCL scaffolds in vivo. (A) Construction of each group of bone defect repair scaffolds by 3D
printing. (B) Subcutaneous implantation in rats. (C) Representative HE-stained images of each group of scaffold sections. (D) Relative number of vessels in
each group of scaffold sections (n = 4/group). (E) Immunofluorescence staining of nuclei (blue), α-SMA (green) and CD31 (red) in each group of scaffold
sections. All experiments were replicated three times. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
staining-positive vessel walls by immunofluorescence or death occurred in any of the rats. X-ray examination
staining (Figure 7E). revealed that the bone defect area in the PRP-GA/PCL
group showed a higher density shadow than that in the
3.8. Bone regeneration effects of 3D-printed blank control group and the GA/PCL group; however, it
biofunctional scaffolds in vivo was significantly lower than that in the PRP-GA@Lap/PCL
We next investigated the osteogenic function of each group group (Figure 8B). Further micro-CT scanning and 3D
of scaffolds by constructing a rat femoral defect model image reconstruction revealed that new bone tissue was
(Figure 8A). After 4 weeks of implantation, no infection observed to grow inward in the area of the bone defects in
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 194 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.702