Page 172 - IJB-9-6
P. 172
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printing in gastroenterology
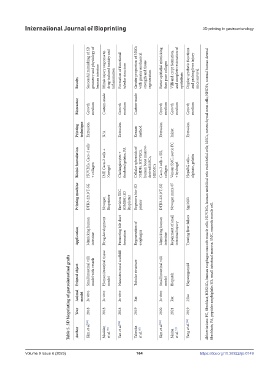
Successful mimicking of 3D geometry and physiology of Mimic injury response to drug-induced toxicity and Formation of functional Greater proportion of MSCs with greater mechanical strength and tissue Better epithelial mimicking than pure collagen Villi and crypt formation, and complete restoration of Display synthetic functions and prolong liver injury
Results human intestine inflammation tubular structure regeneration epithelium mice survival
Bioreactor Growth medium Custom-made Growth medium Custom-made Growth medium Growth medium Growth medium
Printing technique Extrusion N/A Extrusion Kenzan method Extrusion Inkjet Extrusion
Bioink formulation HUVECs, Caco-2 cells + collagen IMF, Caco-2 cells + Novogel Cholangiocytes + thiolated gelatin, PA Cellular spheroids of NHDFs, HUVECs, human bone marrow- derived MSCs, HESMCs Caco-2 cells + SIS, collagen Venous SMC, aortic FC + hydrogel HepaRG cells + alginate, gelatin
Printing machine DTR3-2210 T-SG Novogen Bioprinter Envision TEC (GMBH) 3D Bioplotter Regenova bio-3D printer DTR3-2210 T-SG Novogen mmx-07 Spp1603 Abbreviations: FC, fibroblast; HESMCs, human esophagus smooth muscle cells; HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; NHDFs, normal human dermal
Application Mimicking human intestine Drug development Promoting bile duct formation Regeneration of esophagus Mimicking human intestine Repairment of small intestinal injury Treating liver failure
Table 5. 3D bioprinting of gastrointestinal grafts
Printed object Small intestinal villi model with vessels Human intestinal tissue model Nanostructural scaffold Tubular structure Small intestinal villi model Biopatch Hepatorganoid fibroblasts; PA, peptides amphiphile; SIS, small intestinal mucosa; SMC, smooth muscle cell.
Animal model In vitro In vitro In vitro Rat In vitro Rat Mice
Year 2018 2018 2018 2019 2020 2021 2019
Author Kim et al. [92] Madden et al. [90] Yan et al. [94] Takeoka et al. [89] Kim et al. [93] Maina et al. [91] Yang et al. [96]
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 164 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0149