Page 32 - IMO-2-1
P. 32
Innovative Medicines & Omics Fermentation in dermatology
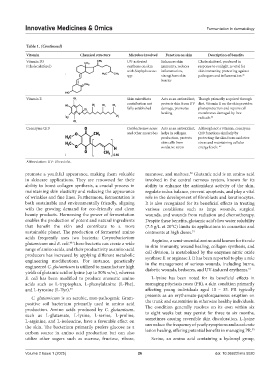
Table 1. (Continued)
Vitamin Chemical structure Microbes involved Function on skin Description of benefits
Vitamin D3 UV-activated Enhances skin Cholecalciferol, produced in
(Cholecalciferol) synthesis on skin immunity, reduces response to sunlight, is vital for
with Staphylococcus inflammation, skin immunity, protecting against
spp. strengthens skin pathogens and inflammation.
45
barrier
Vitamin E Skin microbiota Acts as an antioxidant, Though primarily acquired through
contribution not protects skin from UV diet, Vitamin E on the skin provides
fully established damage, promotes photoprotection and repairs cell
healing membranes damaged by free
radicals.
46
Coenzyme Q10 Cutibacterium acnes Acts as an antioxidant, Although not a vitamin, coenzyme
and other anaerobes helps in collagen Q10 functions similarly by
production, protects protecting the skin from oxidative
skin cells from stress and maintaining cellular
oxidative stress energy levels. 47
Abbreviation: UV: Ultraviolet.
promote a youthful appearance, making them valuable mannose, and maltose. Glutamic acid is an amino acid
50
in skincare applications. They are renowned for their involved in the central nervous system, known for its
ability to boost collagen synthesis, a crucial process in ability to enhance the antioxidant activity of the skin,
maintaining skin elasticity and reducing the appearance regulate redox balance, prevent apoptosis, and play a vital
of wrinkles and fine lines. Furthermore, fermentation is role in the development of fibroblasts and keratinocytes.
both sustainable and environmentally friendly, aligning It is also recognized for its beneficial effects in treating
with the growing demand for eco-friendly and clean various conditions such as large wounds, surgical
beauty products. Harnessing the power of fermentation wounds, and wounds from radiation and chemotherapy.
enables the production of potent and natural ingredients Despite these benefits, glutamic acid’s low water solubility
that benefit the skin and contribute to a more (7.5 g/L at 20°C) limits its applications in cosmetics and
sustainable planet. The production of fermented amino ointments at high doses. 51
acids frequently uses two bacteria: Corynebacterium Arginine, a semi-essential amino acid known for its role
glutamicum and E. coli. These bacteria can create a wide in skin immunity, wound healing, collagen synthesis, and
48
range of amino acids, and their productivity as amino acid cell division, is metabolized by the enzymes nitric oxide
producers has increased by applying different metabolic
engineering modifications. For instance, genetically synthase II or arginase I. It has been reported to play a role
in the management of serious wounds, including burns,
engineered C. glutamicum is utilized to manufacture high diabetic wounds, bedsores, and UV-induced erythema. 52
yields of glutamic acid or lysine (up to 50% w/w), whereas
E. coli has been modified to produce aromatic amino L-lysine has been noted for its beneficial effects in
acids such as L-tryptophan, L-phenylalanine (L-Phe), managing pityriasis rosea (PR), a skin condition primarily
and L-tyrosine (L-Tyr). 49 affecting young individuals aged 10 – 35. PR typically
presents as an erythemato-papulosquamous eruption on
C. glutamicum is an aerobic, non-pathogenic Gram-
positive soil bacterium primarily used in amino acid the trunk and extremities in otherwise healthy individuals.
production. Amino acids produced by C. glutamicum, The condition generally resolves on its own within six
such as L-glutamate, L-lysine, L-serine, L-proline, to eight weeks but may persist for three to six months,
L-arginine, and L-isoleucine, have a favorable effect on sometimes causing reversible skin discoloration. L-lysine
the skin. The bacterium primarily prefers glucose as a can reduce the frequency of yearly symptoms and accelerate
53
carbon source in amino acid production but can also lesion healing, offering potential benefits in managing PR.
utilize other sugars such as sucrose, fructose, ribose, Serine, an amino acid containing a hydroxyl group,
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 26 doi: 10.36922/imo.5020