Page 83 - TD-3-1
P. 83
Tumor Discovery Missense mutations in CXCR1: Impact on stability and function
A
B
C
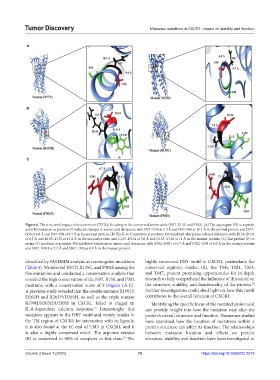
Figure 6. The structural impact of mutations on CXCR1, focusing on the conserved amino acids (N57, R135, and P302). (A) The asparagine (N) to aspartic
acid (D) mutation at position 57 induced changes in amino acid distances, with N57–G56 at 5.9 Å and N57–S58 at 10.4 Å in the normal protein and D57–
G56 at 6.8 Å and D57–S58 at 9.7 Å in the mutant protein. (B) The R-to-C mutation at position 135 exhibited alterations in bond distances, with R135–D134
at 6.5 Å and R135–Y136 at 11.8 Å in the normal protein and C135–D134 at 7.6 Å and C135–Y136 at 11 Å in the mutant protein. (C) The proline (P) to
serine (S) mutation at position 302 exhibited variations in amino acid distances, with P302–N301 at 6.7 Å and P302–I303 at 6.9 Å in the normal protein
and S302–N301 at 7.2 Å and S302–I303 at 8.9 Å in the mutant protein.
identified by FATHMM analysis as carcinogenic mutations highly conserved DRY motif in CXCR1, particularly the
(Table 3). We selected N57D, R135C, and P302S among the conserved arginine residue (R), the TMs, TM1, TM3,
five mutations and conducted a conservation analysis that and TM7, present promising opportunities for in-depth
revealed the high conservation of the N57, R135, and P302 research to fully comprehend the influence of this motif on
74
positions, with a conservation score of 9 (Figure 1A-C). the structure, stability, and functionality of the protein.
A previous study revealed that the double mutants R199H/ Further investigations could shed light on how this motif
D265H and R203H/D265H, as well as the triple mutant contributes to the overall function of CXCR1.
R199H/R203H/D265H in CXCR1, failed to trigger an Identifying the specific locus of the mutated amino acid
IL-8-dependent calcium response. Interestingly, this can provide insight into how the mutation may alter the
72
mutation appears in the DRY motif and mostly resides in protein’s overall structure and function. Numerous studies
the TM region of CXCR1 for interaction with its ligands; have examined how the location of mutations within a
it is also found at the IC end of TM3 in CXCR1, and it protein structure can affect its function. The relationships
is also a highly conserved motif. The arginine residue between mutation location and effects on protein
(R) is conserved in 96% of receptors in this class. The structure, stability, and function have been investigated in
73
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 19 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.2512