Page 84 - TD-3-3
P. 84
Tumor Discovery PTMAP5–hsa-miR-22-3p–KIF2C axis in HCC development
A B
C D E
F G H
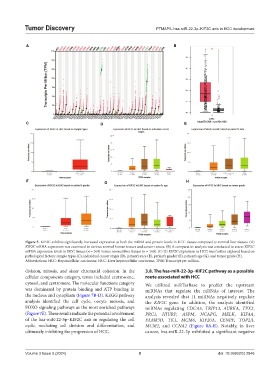
Figure 5. KIF2C exhibits significantly increased expression at both the mRNA and protein levels in HCC tissues compared to normal liver tissues. (A)
KIF2C mRNA expression was examined in various normal human tissues and cancer tissues. (B) A comparative analysis was conducted to assess KIF2C
mRNA expression levels in HCC tissues (n = 369) versus normal liver tissues (n = 160). (C–H) KIF2C expression in HCC was further explored based on
pathological factors: sample types (C), individual cancer stages (D), patient’s race (E), patient’s gender (F), patient’s age (G), and tumor grade (H).
Abbreviations: HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HCC: Liver hepatocellular carcinoma; TPM: Transcript per million.
division, mitosis, and sister chromatid cohesion. In the 3.8. The has-miR-22-3p–KIF2C pathway as a possible
cellular components category, terms included centrosome, route associated with HCC
cytosol, and centromere. The molecular functions category We utilized miRTarBase to predict the upstream
was dominated by protein binding and ATP binding in miRNAs that regulate the mRNAs of interest. The
the nucleus and cytoplasm (Figure 7B-D). KEGG pathway analysis revealed that 11 miRNAs negatively regulate
analysis identified the cell cycle, oocyte meiosis, and the KIF2C gene. In addition, the analysis identified
FOXO signaling pathways as the most enriched pathways miRNAs regulating CDCA5, TRIP13, AURKA, TPX2,
(Figure 7E). These results indicate the potential involvement PRC1, HJURP, ASPM, NCAPG, MELK, KIF4A,
of the hsa-miR-22-3p–KIF2C axis in regulating the cell FAM83D, TK1, MCM6, KIF20A, CENPF, TOP2A,
cycle, mediating cell division and differentiation, and MCM2, and CCNA2 (Figure 8A-R). Notably, in liver
ultimately inhibiting the progression of HCC. cancer, hsa-miR-22-3p exhibited a significant negative
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 8 doi: 10.36922/td.2846