Page 89 - TD-3-3
P. 89
Tumor Discovery PTMAP5–hsa-miR-22-3p–KIF2C axis in HCC development
A
B C
D E
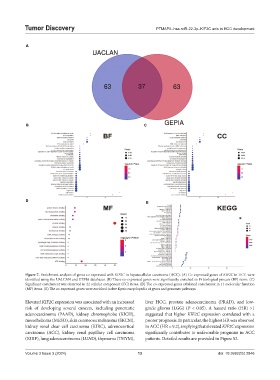
Figure 7. Enrichment analysis of genes co-expressed with KIF2C in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). (A) Co-expressed genes of KIF2C in HCC were
identified using the UALCAN and GEPIA databases. (B) These co-expressed genes were significantly enriched in 19 biological process (BP) items. (C)
Significant enrichment was observed in 22 cellular component (CC) items. (D) The co-expressed genes exhibited enrichment in 11 molecular function
(MF) items. (E) The co-expressed genes were enriched in five Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes pathways.
Elevated KIF2C expression was associated with an increased liver HCC, prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD), and low-
risk of developing several cancers, including pancreatic grade glioma (LGG) (P < 0.05). A hazard ratio (HR) >1
adenocarcinoma (PAAD), kidney chromophobe (KICH), suggested that higher KIF2C expression correlated with a
mesothelioma (MESO), skin cutaneous melanoma (SKCM), poorer prognosis. In particular, the highest HR was observed
kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC), adrenocortical in ACC (HR = 9.2), implying that elevated KIF2C expression
carcinoma (ACC), kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma significantly contributes to unfavorable prognosis in ACC
(KIRP), lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), thymoma (THYM), patients. Detailed results are provided in Figure S2.
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 13 doi: 10.36922/td.2846