Page 157 - AJWEP-22-6
P. 157
Water quality of Bharatpur, Nepal
investigations 11,87-89 have shown that adequate alkalinity
prevents corrosive water conditions and supports
the effectiveness of water treatment processes.
90
The observed values indicate a sufficient buffering
capacity in the groundwater, supporting its stability and
suitability for drinking.
3.1.5. TH
The average TH measured at the IF, RPF, and CF was
137 mg/L, 221 mg/L, and 276 mg/L, respectively, as
shown in Figure 7. The TH ranged between 99 mg/L and
405 mg/L, with the highest value recorded at 405 mg/L
in Sample K near the CF and the lowest hardness at
99 mg/L in Sample C near the IF.
Water hardness traditionally refers to how well
water reacts with soap, with hard water requiring a
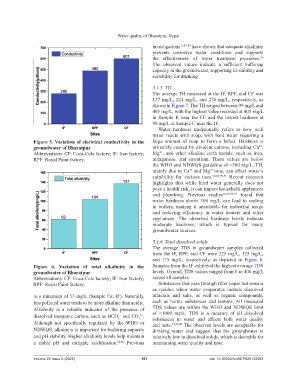
Figure 5. Variation of electrical conductivity in the large amount of soap to form a lather. Hardness is
groundwater of Bharatpur primarily caused by divalent cations, including Ca ,
2+
2+
Abbreviations: CF: Coca-Cola factory; IF: Iron factory; Mg , and other alkaline earth metals, such as iron,
RPF: Royal Paint factory. manganese, and strontium. These values are below
the WHO and NDWQS guideline of <500 mg/L. TH,
mainly due to Ca and Mg ions, can affect water’s
2+
2+
suitability for various uses. 50,60,90,91 Recent research
highlights that while hard water generally does not
pose a health risk, it can impact household appliances
and plumbing. Previous studies 66,69,92,93 found that
water hardness above 300 mg/L can lead to scaling
in boilers, making it unsuitable for industrial usage
and reducing efficiency in water heaters and other
appliances. The observed hardness levels indicate
moderate hardness, which is typical for many
groundwater sources.
3.1.6. Total dissolved solids
The average TDS in groundwater samples collected
from the IF, RPF, and CF were 225 mg/L, 125 mg/L,
and 175 mg/L, respectively, as depicted in Figure 8.
Figure 6. Variation of total alkalinity in the Samples from the IF exhibited the highest average TDS
groundwater of Bharatpur levels. Overall, TDS values ranged from 0 to 400 mg/L
Abbreviations: CF: Coca-Cola factory; IF: Iron factory; across all samples.
RPF: Royal Paint factory. Substances that pass through filter paper but remain
as residue when water evaporates include dissolved
to a minimum of 53 mg/L (Sample Cat IF). Naturally, minerals and salts, as well as organic compounds,
less polluted water tends to be more alkaline than acidic. such as humic substances and tannins. All measured
Alkalinity is a reliable indicator of the presence of TDS values are within the WHO and NDWQS limit
dissolved inorganic carbon, such as HCO and CO . of <1000 mg/L. TDS is a measure of all dissolved
2−
−
substances in water and affects both water quality
3
3
Although not specifically regulated by the WHO or and taste. 57,66,80 The observed levels are acceptable for
NDWQS, alkalinity is important for buffering capacity drinking water and suggest that the groundwater is
and pH stability. Higher alkalinity levels help maintain relatively low in dissolved solids, which is desirable for
a stable pH and mitigate acidification. 80,86 Previous maintaining water quality and taste.
Volume 22 Issue 6 (2025) 151 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025120083