Page 23 - GPD-1-2
P. 23
Gene & Protein in Disease DNA methylation and gene expression on rats with protein malnutrition
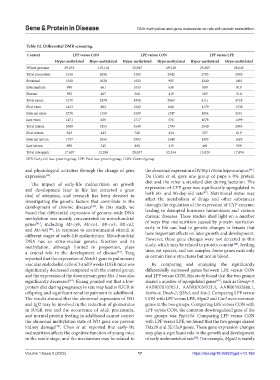
Table 12. Differential DMR screening.
Content LPF versus CON LPE versus CON LPF versus LPE
Hyper‑methylated Hypo‑methylated Hyper‑methylated Hypo‑methylated Hyper‑methylated Hypo‑methylated
Whole genome 29,033 119,116 32,947 19,238 25,365 28,045
Total promoters 3158 2096 3283 2042 2785 2920
Proximal 1568 1028 1682 985 1340 1491
Intermediate 998 661 1033 638 880 919
Distant 592 407 568 419 565 510
Total exons 5170 2879 5958 2869 4111 4728
First exon 1423 882 1542 846 1179 1338
Internal exon 2276 1358 2699 1347 1854 2191
Last exon 1471 639 1717 676 1078 1199
Total intron 3098 1853 3649 1793 2540 2903
First intron 643 443 748 434 557 619
Internal intron 1757 1065 2093 1040 1492 1685
Last intron 698 345 808 319 491 599
Total intergenic 17,607 12,288 20,057 12,534 15,929 17,494
LPE: Early-life low-protein group, LPF: Fetal low-protein group, CON: Control group
[46]
and physiological activities through the change of gene the abnormal expression of PI3Kp110α in hippocampus .
expression . Da Costa et al. gave one group of pups a 0% protein
[39]
The impact of early-life malnutrition on growth diet and the other a standard diet during lactation. The
and development later in life has attracted a great expression of CYP gene was significantly upregulated in
[47]
deal of attention, and research has been devoted to both 60- and 90-day-old rats . Nutritional status may
investigating the genetic factors that contribute to the affect the metabolism of drugs and other substances
development of chronic diseases . In this study, we through the regulation of the expression of CYP enzyme,
[40]
found that differential expression of genome-wide DNA leading to disrupted hormone homeostasis and various
methylation was mainly concentrated on mitochondrial chronic diseases. These studies shed light on a number
genes , including Mt-cyb, Mt-co1, Mt-co3, Mt-co2, of ways that malnutrition caused by protein restriction
[41]
and Mt-nd1 , in response to environmental stimuli at early in life can lead to genetic changes in fetuses that
[42]
different stages of early-life malnutrition. Mitochondrial have important effects on later growth and development.
DNA has an extra-nuclear genetic function and its However, these gene changes were not detected in this
[48]
methylation, although limited in proportion, plays study, which may be related to protein content , feeding
a crucial role in the development of disease . Tang time, rat species, and test samples. Some genes exist only
[43]
reported that the expression of Notch1 gene in pulmonary in certain tissue structures but not in blood.
vascular endothelial cells of 3 and 9 weeks IUGR mice was By comparing and analyzing the significantly
significantly decreased compared with the control group, differentially expressed genes between LPE versus CON
and the expression of the downstream gene Hes-1 was also and LPF versus CON, this study found that the two groups
significantly decreased . Kuang pointed out that a low- shared a number of upregulated genes , such as Gimap-9,
[44]
[49]
protein diet during pregnancy in rats may lead to IUGR in AABR07010705.1, AABR07031521.1, AABR07032888.1,
offspring and significant renal impairment in adulthood. Serinc-4, Dnah-2, Sf3b-5, and Sat-2. Comparing LPF versus
The results showed that the abnormal expression of Wt1 CON with LPF versus LPE, Mgat2 and Car3 were common
and Igf2 may be involved in the reduction of glomerulus genes in the two groups. Comparing LPE versus CON with
in IUGR rats and the occurrence of adult proteinuria, LPF versus CON, the common downregulated gene of the
and normal protein feeding in adulthood cannot correct two groups was Ppp1r3d. Comparing LPF versus CON
the abnormal methylation state of Wt1 gene nor prevent with LPF versus LPE, we found that the two groups shared
kidney damage . Chen et al. reported that early-life Ddx28 and Slc12a9 genes. These gene expression changes
[45]
malnutrition affects the cognitive function of young mice may play a significant role in the growth and development
in the senile stage, and the mechanism may be related to of early malnourished rats . For example, Mgat2 is mainly
[50]
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 17 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.v1i2.169