Page 368 - v11i4
P. 368
International Journal of Bioprinting Sr-doped printed scaffolds for bone repair
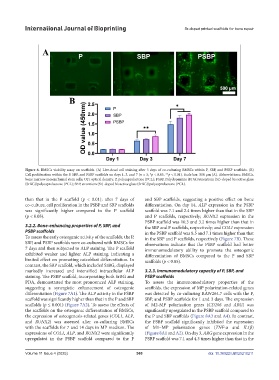
Figure 6. BMSCs viability assay on scaffolds. (A) Live-dead cell staining after 3 days of co-culturing BMSCs within P, SBP, and PSBP scaffolds. (B)
Cell proliferation within the P, SBP, and PSBP scaffolds on days 1, 3, and 7 (n = 3; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Scale bar: 500 μm (A). Abbreviations: BMSCs,
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; OD, optical density; P, polycaprolactone (PCL); PSBP, Polydopamine (PDA)/strontium (Sr)-doped bioactive glass
(SrBG)/polycaprolactone (PCL); SBP, strontium (Sr)-doped bioactive glass (SrBG)/polycaprolactone (PCL).
than that in the P scaffold (p < 0.01); after 7 days of and SBP scaffolds, suggesting a positive effect on bone
co-culture, cell proliferation in the PSBP and SBP scaffolds differentiation. On day 14, ALP expression in the PSBP
was significantly higher compared to the P scaffold scaffold was 7.1 and 2.4 times higher than that in the SBP
(p < 0.05). and P scaffolds, respectively; RUNX2 expression in the
PSBP scaffold was 10.3 and 3.2 times higher than that in
3.2.2. Bone-enhancing properties of P, SBP, and the SBP and P scaffolds, respectively; and COL1 expression
PSBP scaffolds in the PSBP scaffold was 8.5 and 7.1 times higher than that
To assess the early osteogenic activity of the scaffolds, the P, in the SBP and P scaffolds, respectively (Figure 7B). These
SBP, and PSBP scaffolds were co-cultured with BMSCs for observations indicate that the PSBP scaffold had better
7 days and then subjected to ALP staining. The P scaffold immunomodulatory ability to promote the osteogenic
exhibited weaker and lighter ALP staining, indicating a differentiation of BMSCs compared to the P and SBP
limited effect on promoting osteoblast differentiation. In scaffolds (p < 0.05).
contrast, the SBP scaffold, which included SrBG, displayed
markedly increased and intensified intracellular ALP 3.2.3. Immunomodulatory capacity of P, SBP, and
staining. The PSBP scaffold, incorporating both SrBG and PSBP scaffolds
PDA, demonstrated the most pronounced ALP staining, To assess the immunomodulatory properties of the
suggesting a synergistic enhancement of osteogenic scaffolds, the expression of MP polarization-related genes
differentiation (Figure 7A1). The ALP activity in the PSBP was detected by co-culturing RAW264.7 cells with the P,
scaffold was significantly higher than that in the P and SBP SBP, and PSBP scaffolds for 1 and 3 days. The expression
scaffolds (p ≤ 0.001) (Figure 7A2). To assess the effects of of M2-MP polarization genes (CD206 and ARG) was
the scaffolds on the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs, significantly upregulated in the PSBP scaffold compared to
the expression of osteogenesis-related genes (COL1, ALP, the P and SBP scaffolds (Figure 8A3 and A4). In contrast,
and RUNX2) was assessed after co-culturing BMSCs the PSBP scaffold significantly inhibited the expression
with the scaffolds for 7 and 14 days in MP medium. The of M1–MP polarization genes (TNF-α and IL1β)
expressions of COL1, ALP, and RUNX2 were significantly (Figure 8A1 and A2). On day 3, ARG gene expression in the
upregulated in the PSBP scaffold compared to the P PSBP scaffold was 7.1 and 4.3 times higher than that in the
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 360 doi: 10.36922/IJB025210211